To determine if you have an alternator or battery issue, check if the car starts. If it does, it’s likely the alternator.
When your car won’t start or exhibits electrical issues, one of the first questions that arise is whether the alternator or battery is to blame. Both components are crucial to your vehicle’s electrical system, but they serve different functions. Understanding their roles, symptoms of failure, and diagnostic methods can save you time, money, and frustration.
This blog will provide a comprehensive guide to distinguishing between alternator and battery issues and offer practical advice on how to address these problems.
Credit: www.lesschwab.com
Contents
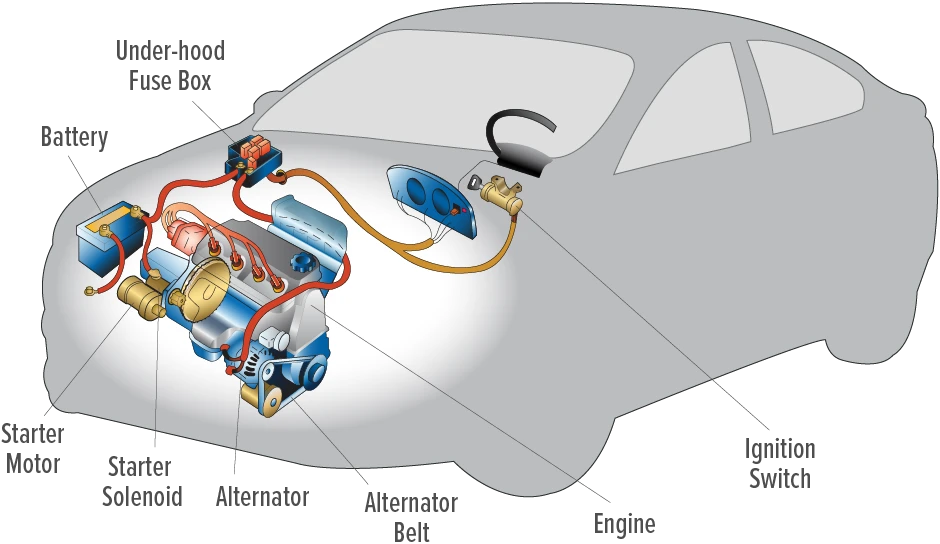
The Role of the Battery
The car battery is the heart of your vehicle’s electrical system. It provides the necessary power to start the engine and supplies energy to the electrical components when the engine is off. Here’s a breakdown of its key functions:
- Starting the Engine: The battery delivers a high current to the starter motor, igniting the engine. Without sufficient battery power, your vehicle won’t start.
- Powering Electrical Components: The battery powers the car’s electrical components, such as lights, radio, and dashboard controls, when the engine is off.
- Voltage Stabilization: The battery helps stabilize voltage fluctuations in the electrical system, protecting sensitive components from damage.
The Role of the Alternator
The alternator works in tandem with the battery but has a different purpose. Once the engine is running, the alternator takes over by:
- Charging the Battery: The alternator recharges the battery while the engine is running, ensuring it has enough power to start the engine again.
- Powering Electrical Systems: It supplies power to the car’s electrical systems when the engine is running, reducing the battery’s load.
- Regulating Voltage: The alternator maintains a consistent voltage level to ensure that electrical components receive a steady supply of power.
Common Symptoms of a Failing Battery
Battery issues are often easier to identify than alternator problems. Here are some common signs that your battery may be at fault:
- Engine Cranks Slowly or Not at All: If the engine turns over slowly or doesn’t crank at all, the battery might not have enough charge.
- Dim Lights: When your headlights or interior lights are dim, especially when the engine is off, it could indicate a weak battery.
- Clicking Noise When Turning the Key: A clicking sound when start the car usually suggests that the battery is too weak to activate the starter motor.
- Corroded Battery Terminals: Visible corrosion on the corroded battery terminals can prevent the battery from delivering power effectively.
- Check Battery Light: Many modern vehicles have a dashboard warning light specifically for battery issues. If this light comes on, it’s time to check the battery.
Common Symptoms of a Failing Alternator
While battery issues are more straightforward, alternator problems can be trickier to diagnose. Here are some signs that your alternator might be failing:
- Dim or Flickering Lights: If your lights dim or flicker while driving, it could be due to an alternator that isn’t supplying enough power.
- Electrical Issues: Malfunctions in electrical components like power windows, radio, or dashboard lights can indicate an alternator problem.
- Dead Battery: A dead battery can be a sign of a failing alternator, especially if the battery is relatively new. If the alternator isn’t charging the battery, it will eventually drain.
- Strange Noises: A failing alternator can produce unusual noises, such as grinding or whining, due to worn-out bearings or other internal issues.
- Battery Warning Light: The battery warning light may come on, not just for battery issues but also when there’s an alternator problem.
Diagnosing the Problem
Determining whether the alternator or battery is the issue requires some diagnostic steps:
- Visual Inspection: Start with a visual inspection of the battery terminals, checking for corrosion or loose connections. Also, look at the alternator belt to ensure it’s not worn or loose.
- Battery Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to check the battery’s voltage. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts with the engine off. If the voltage is below 12.4 volts, the battery may be weak.
- Alternator Output Test: With the engine running, use a multimeter to test the alternator‘s output at the battery terminals. It should read between 13.7 to 14.7 volts. If the voltage is lower, the alternator may not be charging the battery effectively.
- Load Test: A load test can help determine if the battery can hold a charge under a load. This test can be performed at an auto parts store if you don’t have the equipment.
- Check for Parasites: A parasitic draw test can identify if there’s an abnormal drain on the battery when the vehicle is off, which could indicate an electrical issue unrelated to the battery or alternator.

What to Do if the Battery is the Problem
If you determine the battery is at fault, here’s what you can do:
- Charge the Battery: If the battery is simply discharged, you can recharge it using a battery charger. This might resolve the issue if it was due to a temporary drain.
- Replace the Battery: If the battery is old or cannot hold a charge, replacement is the best option. Most batteries last around 3-5 years.
- Clean the Terminals: Corrosion on the terminals can cause poor connections. Cleaning battery corrosion can help restore proper function.
What to Do if the Alternator is the Problem
If the alternator is the culprit, consider the following steps:
- Check the Drive Belt: Ensure the alternator belt is tight and in good condition. A loose or worn belt can prevent the alternator from functioning properly.
- Replace the Alternator: If the alternator is not producing the correct voltage, replacement is likely necessary. This is a more complex repair, often requiring professional assistance.
- Check Electrical Connections: Ensure that all connections to the alternator are secure and free of corrosion. Loose or corroded connections can cause charging issues.
How to Prevent Battery and Alternator Issue
Regular maintenance can help prevent alternator and battery problems:
- Regularly Test the Battery and Alternator: Periodic testing can identify potential issues before they lead to a breakdown.
- Keep Terminals Clean: Regularly inspect and clean battery terminals to prevent corrosion buildup.
- Check Belt Tension and Condition: Regularly inspect the alternator belt for wear and ensure it is properly tensioned.
- Reduce Electrical Load: Avoid using too many electrical components when the engine is off to prevent unnecessary battery drain.
- Drive Regularly: Frequent short trips can prevent the alternator from fully charging the battery. Occasionally taking longer drives can help maintain battery health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about the battery and alternator –
1. Can a bad alternator ruin a new battery?
Yes, a bad alternator can damage a new battery. If the alternator is not charging the battery properly, it can cause the battery to become overcharged or undercharged, leading to premature failure.
2. How long does a car battery last?
A typical car battery lasts between 3 to 5 years, depending on usage, climate, and maintenance. Regular testing can help you anticipate when it might need replacement.
3. Can I drive with a failing alternator?
Driving with a failing alternator is risky. The alternator charges the battery and powers electrical systems while driving. If the alternator fails completely, the car will eventually run out of battery power, leading to a breakdown.
4. What are the signs of a dying car battery?
Signs of a dying battery include slow engine cranking, dim lights, a clicking sound when starting the car, and frequent need for jump-starts.
5. Should I replace the alternator and battery at the same time?
Replacing both at the same time is not always necessary. However, if one fails due to the other’s malfunction, it might be wise to replace both to avoid future issues.
Conclusion
To determine whether it’s an alternator or battery issue, pay attention to the symptoms, such as dimming lights, difficulty starting the engine, or strange sounds. Conduct a visual inspection, check the battery voltage, and perform a charging system test. By understanding the signs and following these steps, you can accurately diagnose and resolve the problem, ensuring your vehicle’s optimal performance and avoiding unnecessary repairs.