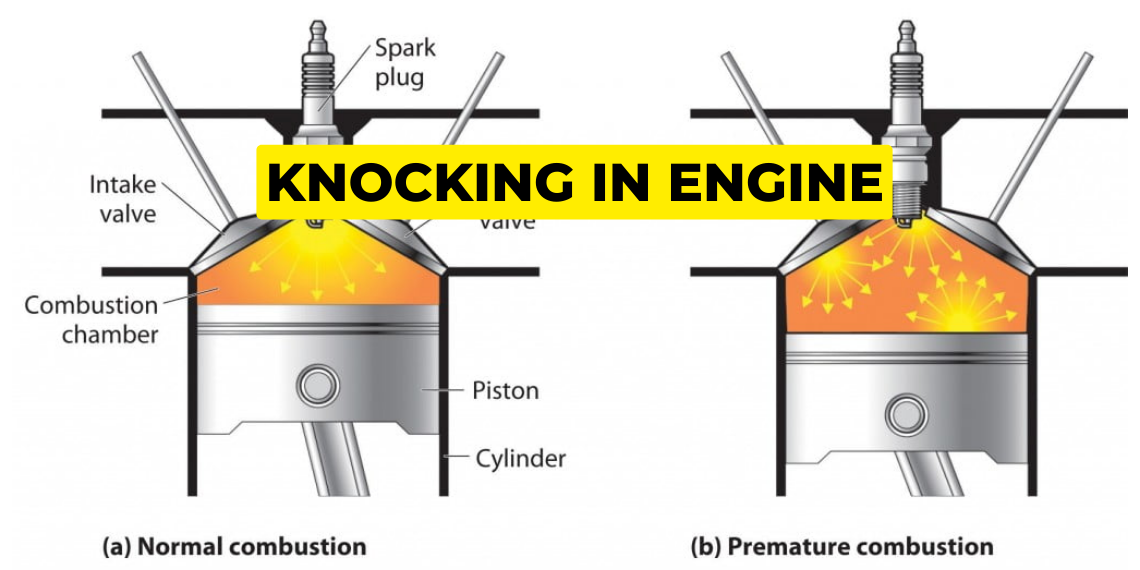
Engine knocking occurs when the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber ignites prematurely, causing a knocking or pinging sound. This can be caused by various factors such as low-quality fuel, incorrect ignition timing, or excessive carbon buildup.
Engine knocking is a common and often alarming issue that can affect vehicles. It manifests as a sharp, metallic sound coming from the engine, usually when accelerating or under load. This knocking, also known as detonation or pinging, indicates abnormal combustion in the engine’s cylinders. Left unchecked, it can lead to significant engine damage.
This comprehensive guide will explore the causes, diagnosis, and solutions for engine knocking to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.

Contents
What is Engine Knocking?
Engine knocking occurs when the air-fuel mixture in one or more of the engine’s cylinders detonates prematurely, or unevenly, instead of burning smoothly in a controlled manner. This results in shock waves that create the distinctive knocking sound. Normally, the combustion process is a controlled explosion that drives the piston down smoothly. However, knocking disrupts this process and can cause various problems.
Causes of Engine Knocking
Here are the common causes of engine knocking –
- Low-Octane Fuel: Using fuel with a lower octane rating than recommended can lead to knocking. Higher octane fuel resists premature detonation.
- Incorrect Air-Fuel Mixture: An imbalance in the air-fuel mixture, often due to faulty fuel injectors, a malfunctioning mass airflow sensor, or a dirty air filter, can cause knocking.
- Carbon Deposits: Over time, carbon deposits can build up on the piston and cylinder walls, increasing compression and leading to knocking.
- Overheating: Excessive engine temperatures can cause the air-fuel mixture to detonate prematurely.
- Faulty Spark Plugs: Spark plugs that are worn out, incorrectly gapped, or have the wrong heat range can cause knocking.
- Timing Issues: Incorrect ignition timing can lead to knocking. If the spark occurs too early or too late, it can cause abnormal combustion.
- Lean Mixture: A lean air-fuel mixture (too much air and not enough fuel) can lead to knocking. This might be due to a vacuum leak, a failing fuel pump, or clogged fuel injectors.
Credit: www.merchantnavydecoded.com
Diagnosing Engine Knocking
Diagnosing engine knocking requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause:
- Listen for Knocking Sounds: Pay attention to when and under what conditions the knocking occurs. Knocking typically happens during acceleration, under load, or at high RPMs.
- Check Fuel Quality: Ensure you are using the recommended octane fuel. If you suspect fuel quality issues, try using a higher octane fuel to see if the knocking subsides.
- Inspect Spark Plugs: Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Look for signs of wear, damage, or incorrect gaps. Replace them if necessary with the correct type and heat range.
- Check the Air-Fuel Mixture: Use a diagnostic tool to check the air-fuel ratio. Look for any error codes related to the fuel system or sensors that might indicate a problem.
- Inspect for Carbon Deposits: If possible, inspect the combustion chambers for carbon buildup. This might require removing the cylinder head.
- Check Engine Timing: Use a timing light to check the ignition timing. Ensure it is set according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Monitor Engine Temperature: Ensure the engine cooling system is functioning properly and that the engine is not overheating. Check the radiator, coolant levels, and thermostat.
How to Fix Engine Knocking
Once you’ve identified the cause of engine knocking, you can implement the appropriate solutions:
- Use Higher Octane Fuel: If low-octane fuel is the cause, switch to a higher octane fuel that meets or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Clean or Replace Spark Plugs: Replace worn-out or incorrectly gapped spark plugs with the correct type. Regularly inspect and maintain your spark plugs.
- Adjust the Air-Fuel Mixture: Ensure the air-fuel mixture is balanced. Clean or replace the air filter, inspect fuel injectors, and check sensors like the mass airflow sensor and oxygen sensor.
- Remove Carbon Deposits: Use a fuel system cleaner that can help remove carbon deposits. In severe cases, you might need to physically clean the combustion chambers.
- Fix Overheating Issues: Address any issues causing the engine to overheat. Ensure the cooling system is functioning properly, and replace any faulty components.
- Adjust Ignition Timing: Correct the ignition timing if it is off. Consult your vehicle’s service manual for the correct procedure.
- Repair Vacuum Leaks and Fuel System Issues: Identify and repair any vacuum leaks. Ensure the fuel system components, like the fuel pump and fuel injectors, are functioning correctly.

Preventing Engine Knocking
Prevention is key to avoiding engine knocking and the potential damage it can cause:
- Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, including regular oil changes, spark plug replacements, and air filter changes.
- Use the Right Fuel: Always use the recommended octane fuel for your vehicle. Higher performance engines often require higher octane fuel to prevent knocking.
- Monitor Engine Temperature: Keep an eye on your engine’s temperature gauge and address any cooling system issues promptly.
- Keep the Fuel System Clean: Use fuel system cleaners periodically to prevent carbon buildup and keep fuel injectors clean.
- Inspect and Replace Spark Plugs: Regularly inspect spark plugs and replace them as needed to ensure proper combustion.
- Check for Software Updates: Some vehicles might have software updates available that can address timing or fuel management issues. Check with your dealer or manufacturer.
When to Seek Professional Help
While some causes of engine knocking can be addressed with basic maintenance and troubleshooting, others may require professional assistance. If you’re unable to identify or resolve the knocking, or if the problem persists despite your efforts, it’s best to seek help from a qualified mechanic. Persistent knocking can lead to serious engine damage if left unchecked.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about the engine knocking –
How Does Engine Knocking Affect My Vehicle?
Engine knocking can lead to reduced engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and potential damage to the engine if left unaddressed.
Can Engine Knocking Be Fixed?
Yes, engine knocking can be fixed by using higher-quality fuel, adjusting the ignition timing, performing regular maintenance, or replacing worn-out engine components.
Is Engine Knocking A Sign Of A Serious Problem?
Engine knocking can indicate underlying issues with your vehicle’s engine. It’s important to address the problem promptly to prevent further damage and ensure optimal engine performance.
Conclusion
Addressing engine knocking promptly is crucial for vehicle longevity. Regular maintenance and using high-quality fuel can prevent this issue. Don’t ignore strange noises; consult a mechanic for proper diagnosis and repairs. Stay proactive to keep your engine running smoothly and efficiently.