An engine works by burning fuel to create power that moves the vehicle. This combustion process drives pistons up and down, which in turn rotates the crankshaft to generate motion.
Engines are the heart of any vehicle, converting fuel into energy to propel it forward. Understanding how an engine works is key to comprehending the intricacies of automotive engineering. By harnessing the power of combustion, engines efficiently convert chemical energy into mechanical force.
Whether it’s a gasoline engine or a diesel engine, the fundamental principle remains the same – controlled explosions driving pistons to generate movement. Join us as we delve deeper into the fascinating world of engines and unravel the magic that powers our vehicles.

Credit: haynes.com
Contents
The Heart Of The Machine: Anatomy Of An Engine
When it comes to understanding how an engine works, it’s essential to delve into the intricate details of its anatomy. An engine can be likened to the heart of a machine, driving its power and performance. By exploring the key components and the combustion process, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the marvels of engineering that make engines run.
Key Components And Their Roles
An engine is a complex assembly of various components, each playing a crucial role in its operation. Let’s take a closer look at the key components and their functions:
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Piston | Converts the energy from the combustion process into mechanical motion. |
| Cylinder | Provides a sealed chamber where the combustion process occurs. |
| Spark Plug | Ignites the air-fuel mixture to initiate the combustion process. |
| Crankshaft | Converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion. |
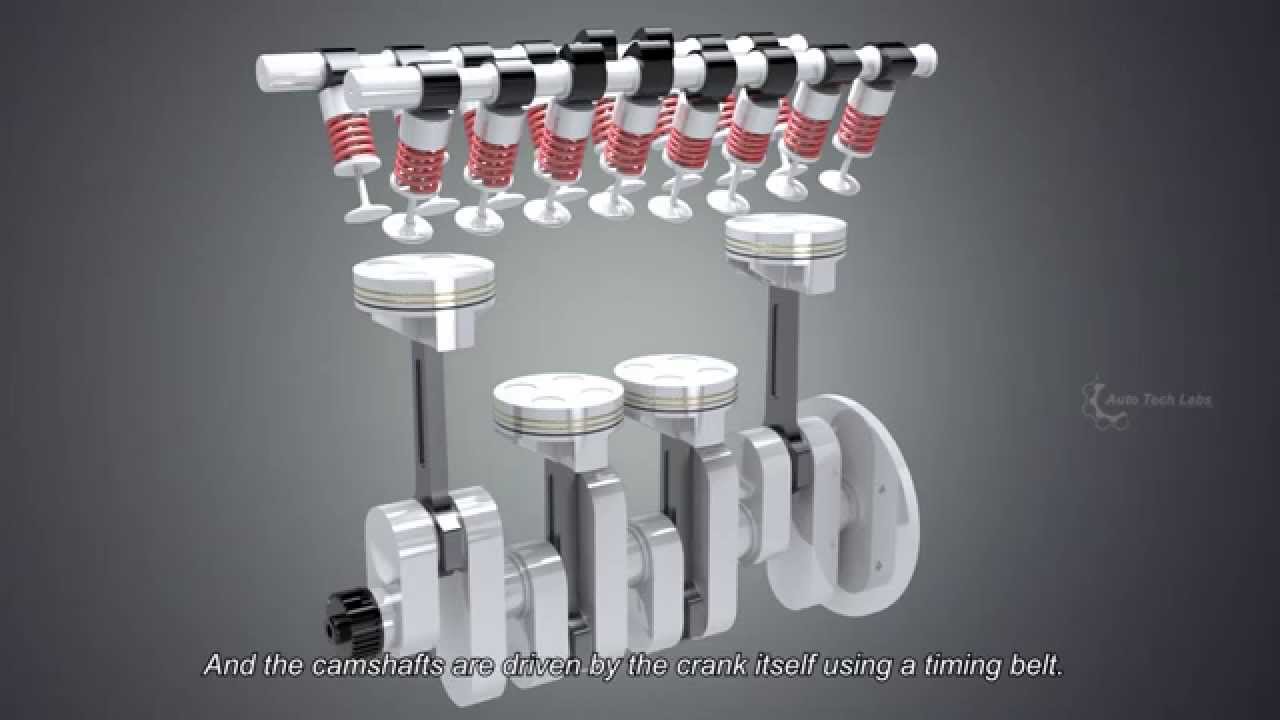
| Camshaft | Controls the opening and closing of valves to regulate airflow. |
| Valves | Allow the intake and exhaust of air and fuel, as well as the expulsion of exhaust gases. |
| Connecting Rod | Transfers motion from the piston to the crankshaft. |
These components work together in a precise sequence to ensure the engine functions efficiently and generates power.
The Combustion Process
The combustion process is the heart of an engine, responsible for converting fuel into energy. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the combustion process:
- Air and fuel are mixed together in the combustion chamber.
- The spark plug ignites the air-fuel mixture, causing a controlled explosion.
- The explosion generates high pressure, forcing the piston downward.
- As the piston moves, it transfers energy to the crankshaft through the connecting rod.
- The crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion.
- The rotational motion is then transferred to the wheels of a vehicle or used to power other machinery.
This continuous cycle of combustion and mechanical motion is what enables an engine to power a wide range of vehicles and equipment.
From Fuel To Motion: The Journey Of Energy
From Fuel to Motion: The Journey of Energy
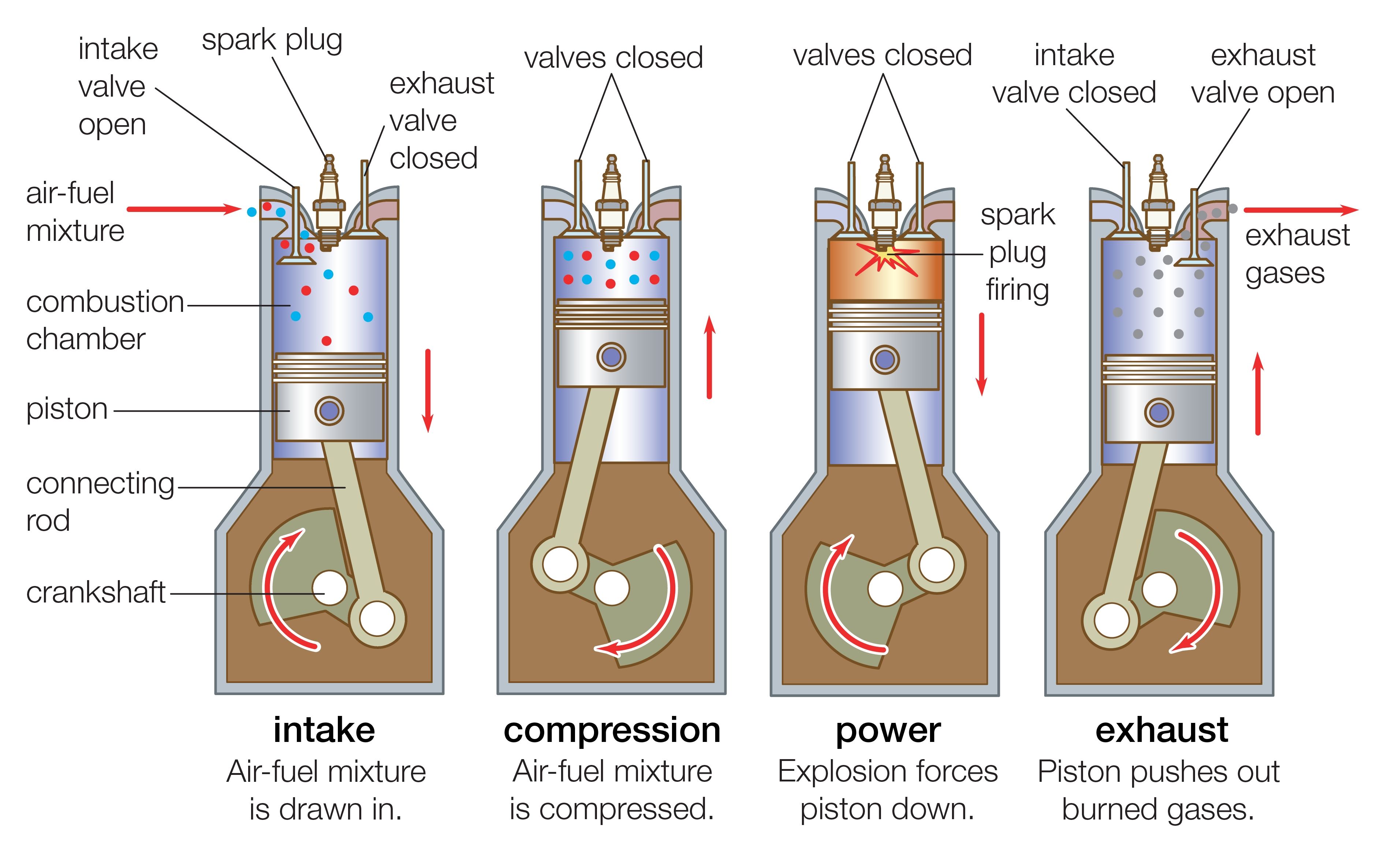
The Four-stroke Cycle Explained
The four-stroke cycle is a fundamental process in the functioning of internal combustion engines. It involves four distinct stages: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. Each stroke plays a crucial role in converting fuel into motion, propelling vehicles forward.
Turning Chemical Energy Into Mechanical Power
Engines utilize the energy stored in fuel to generate mechanical power. This transformation occurs through a series of complex processes, including combustion, expansion, and conversion of heat energy into kinetic energy. The result is the driving force that moves vehicles and powers machinery.
Innovations And Evolutions In Engine Technology
Innovations and Evolutions in Engine Technology have transformed the way we power vehicles, with advancements that have revolutionized performance, efficiency, and environmental impact.
Breaking Barriers With Turbocharging
Turbocharging has broken barriers in engine technology, enhancing power and efficiency. By utilizing exhaust gases to drive a turbine, turbochargers force more air into the combustion chamber, resulting in increased power output without a significant increase in engine size.
The Future: Electric And Hydrogen Engines
The future of engine technology lies in electric and hydrogen engines. Electric engines offer zero-emission propulsion, while hydrogen engines produce electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, emitting only water vapor. These innovations mark the next phase in sustainable transportation.
Credit: www.caranddriver.com

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does An Engine Work?
An engine works by converting fuel into mechanical energy through combustion and internal processes.
What Are The Main Engine Components?
The main components of an engine include the cylinder block, pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, valves, and fuel system.
Why Is Engine Oil Important?
Engine oil is crucial for lubricating moving parts, reducing friction, cooling the engine, and preventing corrosion and wear.
What Is The Role Of The Fuel System?
The fuel system is responsible for delivering the correct amount of fuel to the engine for combustion.
How Often Should Engine Oil Be Changed?
Engine oil should typically be changed every 3,000 to 5,000 miles or as recommended in the owner’s manual.
Conclusion
Understanding how an engine works is essential knowledge for any car enthusiast or aspiring mechanic. From the intake of air and fuel to the combustion process and the expulsion of exhaust gases, each component plays a crucial role in the engine’s functionality.
By grasping these fundamental principles, one can appreciate the complexity and ingenuity behind this remarkable piece of machinery. So, the next time you start your car, take a moment to marvel at the intricate workings happening under the hood.