A timing belt size chart lists the belt’s key specs, like length, tooth count, and pitch, to ensure a proper fit for the engine. Using the correct size prevents engine damage and ensures optimal performance. Always refer to your vehicle’s manual for the right specifications.
The timing belt plays an important role in the operation of the vehicle’s engine, connecting the crankshaft and the camshaft to ensure the precise timing of the engine’s valves. Without a properly functioning timing belt, your engine may not run at all—or worse, the belt could break, causing extensive damage to the engine. To keep your vehicle running smoothly, it’s essential to understand how to select the right timing belt, which is where a timing belt size chart becomes indispensable.
In this blog post, we will explore the concept of timing belt size charts, their importance, how to read them, and how to choose the correct size for the vehicle.
Contents
- 1 Why is the Timing Belt Size Important?
- 2 Key Components of a Timing Belt Size Chart
- 3 How to Read a Timing Belt Size Chart
- 4 Timing Belt Replacement Process
- 5 Factors to Consider When Choosing a Timing Belt Size
- 6 Timing Belt Size Chart Example
- 7 Why Timing Belt Size Charts Matter
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions
- 9 Conclusion
Why is the Timing Belt Size Important?
The size of the timing belt is essential because it must match the specifications set by the manufacturer of your vehicle’s engine. A belt that is too small or too large can cause engine malfunction, damage to the belt, and ultimately lead to costly repairs. Ensuring the correct size helps to:
- Maintain Engine Performance: A well-sized timing belt ensures smooth engine operation and maximizes fuel efficiency.
- Prevent Engine Damage: An incorrect size can cause the belt to slip or break, potentially leading to catastrophic damage to engine components.
- Extend Belt Life: The correct fit reduces wear and tear on the belt, extending its service life.
- Promote Proper Timing: Accurate synchronization between the crankshaft and camshaft is critical for engine timing and performance.
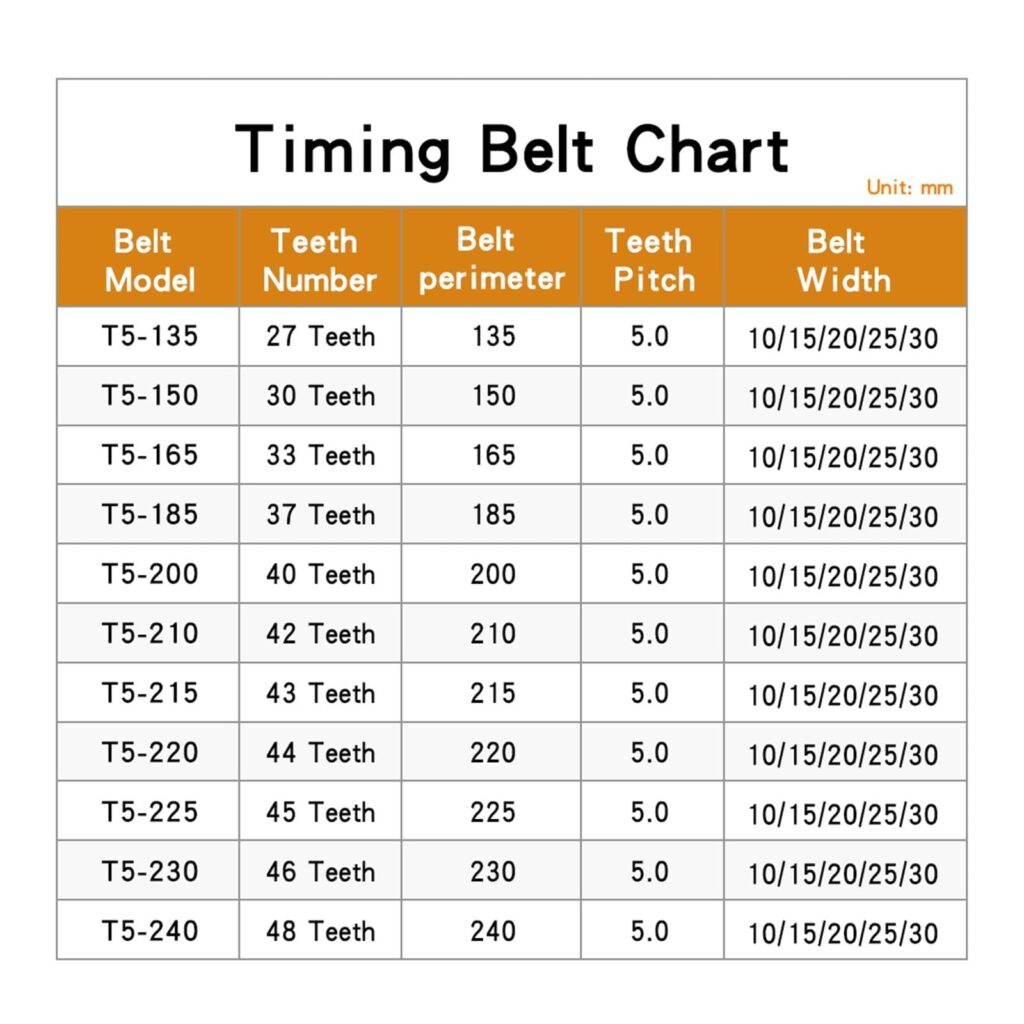
Key Components of a Timing Belt Size Chart
A timing belt size chart typically includes various specifications that help you select the correct belt for your vehicle. These key components include:
- Belt Length: The total length of the timing belt, usually measured in millimeters (mm). It indicates how long the belt is from end to end when laid flat.
- Tooth Count: The number of teeth on the inside of the belt. Each tooth corresponds to a specific gear or sprocket.
- Pitch: The distance between the teeth, usually measured in millimeters. The pitch determines how tightly the teeth mesh with the sprockets.
- Width: The width of the belt, often indicated in millimeters. A wider belt typically has more teeth and is stronger.
- Belt Profile: The shape and design of the teeth, which can vary. Common profiles include trapezoidal and curvilinear shapes.
How to Read a Timing Belt Size Chart
Timing belt size charts can seem overwhelming at first, but once you understand the key components, reading them becomes a straightforward task. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to interpret the chart:
- Locate Your Vehicle’s Information: The first step in selecting the correct timing belt is to know your vehicle’s make, model, and engine type. This information is usually available in your vehicle’s owner manual or online.
- Find the Belt’s Specifications: Once you have the vehicle details, look up the timing belt specifications in the chart. The chart will list the length, tooth count, pitch, and width of each compatible timing belt for your engine.
- Compare Specifications: Match the specifications of the timing belt from the chart with the original part number or the specifications provided by the vehicle manufacturer. Pay close attention to the belt length, tooth count, and pitch to ensure the best fit.
- Cross-Reference with OEM or Aftermarket Parts: If you’re buying a replacement belt, compare the size chart to your original equipment manufacturer (OEM) or aftermarket parts catalog to ensure compatibility.
Timing Belt Replacement Process
When replacing the timing belt, it’s important to follow the vehicle manufacturer’s recommended service intervals, usually between 60,000 and 100,000 miles, depending on the type of engine and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Replacing the timing belt typically involves removing several components to access the belt, including the timing cover, pulleys, and sometimes the water pump. It’s essential to use the correct size belt to ensure it meshes perfectly with the sprockets. If you’re replacing the belt yourself, always refer to a timing belt size chart for accurate specifications.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Timing Belt Size
Here are a few factors to consider when selecting the right timing belt for your engine:
- Engine Type and Configuration: The size and design of the timing belt vary depending on whether the engine is a single overhead cam (SOHC), dual overhead cam (DOHC), or another configuration.
- Vehicle Manufacturer Recommendations: Always consult your vehicle’s manual or manufacturer to get the proper timing belt specifications.
- Belt Material: Timing belts are typically made of rubber, but some may have synthetic reinforcements or Kevlar for added strength and durability. Ensure you choose a belt with the appropriate material to match your driving conditions.
- Belt Replacement Kit: Many mechanics recommend replacing the timing belt and related components such as tensioners and pulleys at the same time. Timing belt kits often include everything you need for a complete replacement.
Timing Belt Size Chart Example
Let’s consider a simplified example of a timing belt size chart:
| Make | Model | Year | Engine Type | Belt Length (mm) | Tooth Count | Pitch (mm) | Width (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota | Camry | 2010 | 2.5L DOHC | 1000 | 128 | 9.525 | 22 |
| Honda | Civic | 2012 | 1.8L SOHC | 950 | 116 | 9.525 | 20 |
| BMW | 328i | 2015 | 2.0L DOHC | 1025 | 130 | 9.525 | 22 |
Why Timing Belt Size Charts Matter
Using the correct timing belt size is critical for the longevity and performance of your engine. A well-maintained timing belt will last for many years, but improper sizing or an old, worn-out belt can lead to significant engine damage.
By using a timing belt size chart, you ensure that you’re installing the correct part, helping your engine run smoothly and avoiding the risk of costly breakdowns.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about timing belt size chart –
1. How do I know when to replace my timing belt?
The timing belt should generally be replaced every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on your vehicle’s manufacturer recommendations. Signs that you need a new timing belt include unusual engine noises, difficulty starting the engine, or if the engine stalls.
2. Can I drive my car if the timing belt is worn out?
Driving with a worn-out timing belt is risky and can cause the belt to snap, leading to severe engine damage. It’s best to replace the timing belt as recommended by your vehicle manufacturer.
3. How do I find the correct timing belt size for my car?
To find the right size, consult the timing belt size chart for your vehicle’s make, model, and engine type. You can usually find the chart in your vehicle’s manual or by searching online for your vehicle’s specifications.
4. What happens if I use the wrong size timing belt?
Using the wrong size timing belt can cause improper engine timing, leading to poor engine performance, overheating, and potential damage to the engine’s valves, pistons, or other components.
5. Can I replace the timing belt myself?
Replacing a timing belt requires special tools and knowledge. If you’re confident in your mechanical skills and have access to the correct tools, you can replace it yourself. However, it’s often recommended to have a professional mechanic perform the replacement to ensure it’s done correctly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the correct timing belt size is crucial for your engine’s performance and longevity. Refer to the timing belt size chart and follow manufacturer specifications to avoid engine damage and ensure proper timing. Regular maintenance and timely replacements will keep your vehicle running smoothly for years to come. If you’re unsure about replacing the belt yourself, a professional mechanic can ensure the job is done right.