A VW engine identification chart uses engine codes to provide details like displacement, power, and model application. The engine code, found on the block or service sticker, helps with part compatibility and maintenance. It’s essential for identifying engines, especially in restorations or swaps.
Volkswagen (VW) has a storied history of manufacturing reliable, innovative, and efficient engines for a wide variety of vehicles. For enthusiasts, mechanics, and restorers, the ability to accurately identify the engine in a VW vehicle is critical. The VW engine identification chart provides essential details about engine codes, their applications, and specifications. Knowing the engine code of your VW helps determine compatibility for parts, diagnostics, and restorations.
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into how to use a VW engine identification chart effectively. We will explore engine codes, how to find them, their significance, and common applications in popular VW models.
Contents
VW Engine Codes
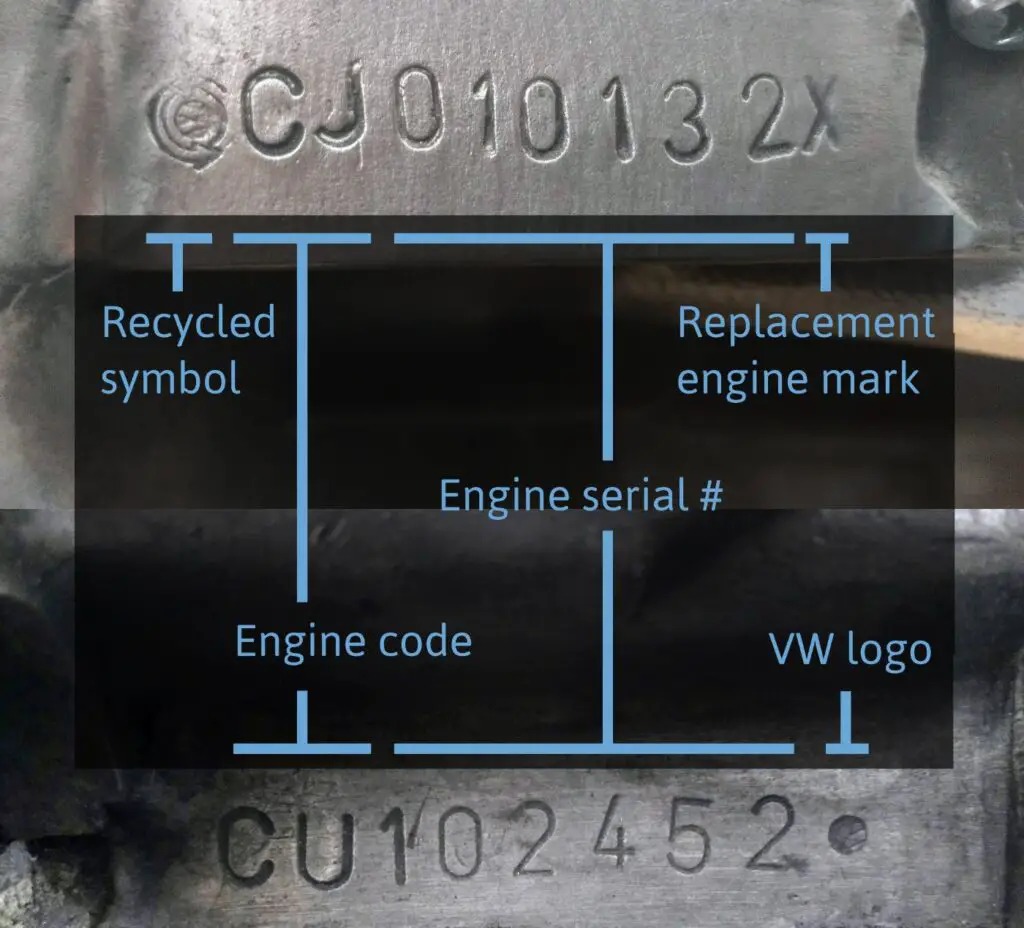
Volkswagen engine codes are alphanumeric sequences that provide vital information about the engine, including its type, size, fuel system, and sometimes the year of manufacture. These codes are typically stamped on the engine block and can also be found in the vehicle’s service book or data sticker.
Breakdown of a Typical VW Engine Code
- Example Code: CBFA
- C: This character usually represents the engine family.
- B: This letter may denote the engine’s variant or version.
- FA: These letters typically indicate a specific configuration or features, such as emissions standards.
Each code is unique to a specific engine model, making it an essential tool for identifying the engine for maintenance or upgrades. Engine codes can be especially useful when you are unsure about the engine’s origin or if the car has undergone an engine swap.
Where to Find the Engine Code
There are a few common places where the VW engine code can be found:
- Engine Block: The engine code is usually stamped on the engine block. For air-cooled engines, you can often find it near the crankshaft pulley or the fuel pump.
- Service Book: The vehicle’s service book may include the engine code along with other important identification numbers.
- Data Sticker: A data sticker located in the trunk (typically near the spare tire compartment) or inside the driver’s door may also contain the engine code.
For modern vehicles, the engine code may also be retrievable through an OBD-II scanner. This can make it easier to verify the code in case it’s not visible on the block.

Decoding the Volkswagen Engine Identification Chart
The engine identification chart lists engine codes along with key details about each engine, such as:
- Displacement (Size): Usually measured in liters or cubic centimeters (cc), displacement indicates the total volume of the engine’s cylinders.
- Power Output (Horsepower): This tells you how powerful the engine is.
- Fuel Type: Indicates whether the engine runs on gasoline (petrol), diesel, or other fuels.
- Aspiration: Specifies if the engine is naturally aspirated or turbocharged (T).
- Application: Refers to the VW models the engine was installed in.
Below is a sample breakdown of a few notable VW engine codes:
| Engine Code | Displacement | Power (HP) | Fuel Type | Aspiration | Models |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEB | 1.8L | 150 | Gasoline | Turbocharged | Passat B5, Audi A4 |
| ALH | 1.9L | 90 | Diesel | Turbocharged | VW Golf Mk4, VW Jetta |
| CBFA | 2.0L | 200 | Gasoline | Turbocharged | VW GTI, Passat, Audi A3 |
| AEH | 1.6L | 100 | Gasoline | Naturally Aspirated | VW Golf Mk4, VW Bora |
| BGD | 2.0L | 136 | Diesel | Turbocharged | VW Passat, VW Golf Mk5 |
Air-Cooled Engines
Volkswagen’s air-cooled engines are legendary, powering vehicles like the VW Beetle, Type 2 (Bus), and Karmann Ghia. These engines have a separate identification system, typically starting with a single or double letter followed by numbers. For instance:
- H5: A 1500cc engine commonly found in late 1960s Beetles.
- AE: A 1600cc engine with dual-port heads, often found in later Beetles and Type 2 Buses.
Common Volkswagen Engine Families
Volkswagen engines can generally be grouped into several major families. Here’s a breakdown of some of the most popular families:
Air-Cooled Engines (Pre-1975)
Volkswagen’s air-cooled engines were integral to the company’s identity. These engines are identified by engine numbers that start with one or two letters, followed by numbers.
- 1.1L to 1.6L Engines: Found in models like the Beetle and Karmann Ghia.
- T1 and T2 Engines: Found in the Type 1 and Type 2 Buses.
Water-Cooled Engines (Post-1975)
After the mid-1970s, VW transitioned to water-cooled engines. These engines are more efficient, and powerful, and allowed VW to expand its lineup.
- EA827 Family: One of the most popular water-cooled engine families, which powered the VW Golf, Jetta, and Passat models.
- EA113 Family: Known for its high-performance variants, this family included 1.8L and 2.0L turbocharged engines found in vehicles like the VW GTI and Audi A4.
Diesel Engines
Volkswagen is well-known for its robust diesel engines, particularly the TDI (Turbocharged Direct Injection) series.
- 1.9L TDI (ALH): Widely regarded for its reliability, found in the Golf, Jetta, and Passat.
- 2.0L TDI: Found in more modern VW vehicles, providing more power and efficiency than its predecessors.
How to Use a VW Engine Identification Chart
To use a VW engine identification chart effectively, follow these steps:
- Locate the Engine Code: Start by finding your engine code using the methods discussed earlier.
- Match the Code to the Chart: Refer to the VW engine identification chart and find the engine code. The chart will give you detailed information about the engine, including displacement, fuel type, and application.
- Check Compatibility: If you’re looking for parts or planning a restoration, ensure that the engine code matches the vehicle’s original equipment. This will help avoid compatibility issues.
Evolution of VW Engines Over Time
Volkswagen’s engine designs have evolved significantly over the decades, moving from air-cooled to water-cooled technology, increasing in power, and improving emissions. Early engines, such as the classic air-cooled flat-four “boxer” engines, were simple, easy to repair, and beloved by enthusiasts. The shift to water-cooled engines in the 1970s marked a change towards more modern, efficient, and powerful designs.
In recent years, VW has focused on developing more advanced engines, including turbocharged gasoline engines, direct-injection systems, and hybrid powertrains. This makes the VW engine identification chart even more essential as the range of engines has become more diverse.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about VW engine identification chart –
1. Where can I find my VW engine code?
You can find the VW engine code stamped on the engine block, typically near the crankshaft pulley or fuel pump for older models. For newer models, the code may also be located in the service book, data sticker, or retrievable via OBD-II scanners.
2. What do the letters in VW engine codes mean?
The letters in VW engine codes represent various aspects of the engine, such as the engine family, variant, and specific configurations. The first character often denotes the engine family, while subsequent characters may indicate specific features like emissions standards or engine power output.
3. Are VW air-cooled engines still available today?
While Volkswagen no longer manufactures air-cooled engines, they remain popular among collectors, restorers, and enthusiasts, especially for classic models like the Beetle and VW Bus. You can find rebuilt and remanufactured air-cooled engines through specialized vendors.
4. How do I know if a part is compatible with my VW engine?
To ensure part compatibility, always refer to your engine code. Once you have the engine code, use a VW engine identification chart or consult a parts catalog to verify if the part you need is compatible with your engine and vehicle model.
5. Can a VW engine code tell me the year of the engine?
While the engine code doesn’t directly include the manufacturing year, certain codes are associated with specific model years or ranges. Cross-referencing the engine code with production data in a VW engine chart can help narrow down the engine’s manufacturing year.
Conclusion
Volkswagen’s diverse array of engines over the decades requires enthusiasts and professionals alike to use engine identification charts effectively. Knowing your engine code and matching it to the correct specifications ensures proper maintenance, part compatibility, and better performance. Whether you’re working with a classic air-cooled VW or a modern TDI, the engine identification chart is an invaluable resource for understanding and maintaining your vehicle.