W engines have a compact, four-bank design for higher power, used in luxury and performance cars, but they are more complex and less fuel-efficient. V engines, with two banks, are simpler, more common, and used in a wider range of vehicles.
Engines are the heart of any automobile, and among the many different engine configurations, the “W” and “V” engines stand out as some of the most powerful and sophisticated designs. The distinction between a W engine and a V engine goes beyond their shapes and layouts, influencing everything from performance to design complexity.
This blog post delves into the differences, advantages, and applications of these two engine configurations, providing a comprehensive comparison of the W and V engines.
Contents
What is a V Engine?
The V engine, also known as a V-type engine, is one of the most common engine configurations used in a wide variety of vehicles, from small cars to high-performance sports cars and trucks. It is named after the “V” shape formed by its cylinder arrangement. In a V engine, the cylinders are arranged in two banks that form an angle with each other, typically between 60 and 90 degrees. The engine’s crankshaft runs between these two banks, and each cylinder bank houses an equal number of cylinders.
Common Variants of the V Engine
The most common variants of the V engine include:
- V6: A 6-cylinder engine with two banks of three cylinders each. Commonly used in mid-sized cars and SUVs.
- V8: An 8-cylinder engine with two banks of four cylinders. Popular in performance cars, trucks, and muscle cars.
- V10: A 10-cylinder engine found in high-performance sports cars and trucks.
- V12: A 12-cylinder engine with two banks of six cylinders. Known for its smooth operation, often used in luxury and high-performance
Key Features of a V Engine
Here are the key features of a V engine:
- Configuration: The V engine consists of two banks of cylinders arranged in a “V” shape, typically at angles ranging from 60 to 90 degrees. This design allows for a compact engine layout.
- Cylinder Count: V engines commonly come in various configurations, including V6, V8, V10, and V12, allowing for a range of power outputs and performance characteristics.
- Balance and Smoothness: V engines, especially V8 and V12 configurations, are known for their balanced performance and smooth operation due to even firing intervals, reducing vibration.
- Torque and Power: V engines typically deliver high torque and power, making them suitable for various applications, from passenger cars to heavy-duty trucks and performance vehicles.
- Versatility: The V engine design is versatile, enabling it to fit in a wide range of vehicles, from compact cars to luxury sedans and SUVs.
- Maintenance and Repair: V engines are generally easier to maintain compared to more complex engine configurations like W engines, often resulting in lower repair costs.
- Fuel Efficiency: While V engines can be less fuel-efficient than inline engines, configurations like the V6 can offer a good balance between performance and fuel economy.
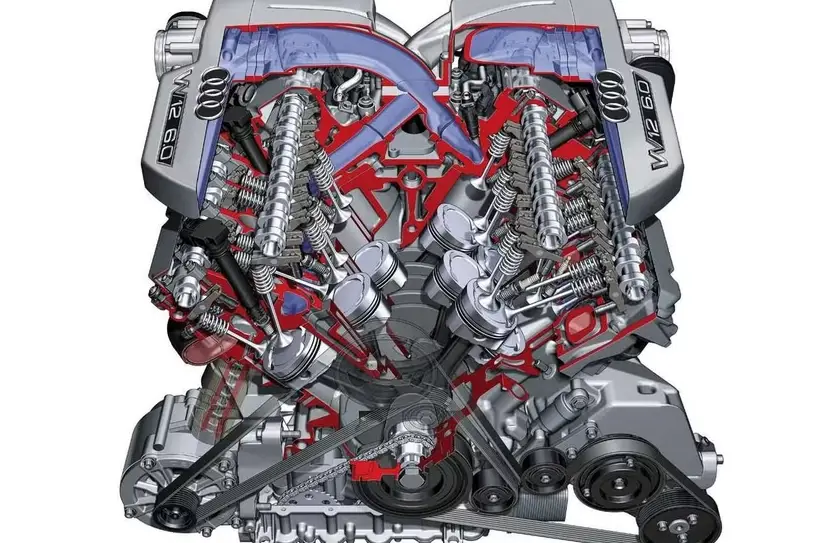
What is a W Engine?
A W engine, also known as a W-type engine, is a more complex and less common configuration compared to the V engine. It gets its name from the “W” shape formed by its cylinder banks. The W engine essentially merges two V engines, with four banks of cylinders instead of two. This allows for a more compact engine design with a greater number of cylinders without significantly increasing the engine’s overall size.
The W engine is best known for being used in high-end luxury cars and performance vehicles. One of the most famous examples of a W engine is Volkswagen’s W12 engine, which has been used in cars like the Bentley Continental GT and the Bugatti Veyron.
Common Variants of the W Engine
Here are the common variants of the W engine:
- W8: A compact 8-cylinder engine with two banks of four cylinders. It’s typically used in smaller luxury cars and performance vehicles, offering a balance of power and efficiency.
- W12: A 12-cylinder engine that combines two V6 engines. It is known for its smooth operation and high power output, commonly found in luxury and high-performance cars like the Bentley Continental GT.
- W16: A 16-cylinder engine that combines two V8 engines, used primarily in supercars such as the Bugatti Veyron and Chiron. It delivers exceptional power, often exceeding 1,500 horsepower, and is designed for maximum performance.
Key Features of a W Engine
Here are the key features of a W engine:
- Configuration: The W engine consists of four banks of cylinders arranged in a “W” shape, allowing for a compact design that accommodates a high cylinder count without significantly increasing the engine’s overall size.
- High Cylinder Count: W engines typically have a larger number of cylinders, such as W8, W12, and W16 configurations, which contribute to higher power output and performance.
- Power and Performance: W engines are known for their ability to deliver exceptional power, making them popular in high-performance and luxury vehicles. For example, the W16 engine in the Bugatti Veyron produces over 1,500 horsepower.
- Smooth Operation: The design of W engines allows for balanced power delivery and reduced vibration, leading to a smoother and more refined driving experience compared to many other engine types.
- Compact Size: Despite having a high cylinder count, W engines maintain a relatively compact footprint, allowing them to fit in tight engine bays without sacrificing performance.
- Complexity and Cost: The intricate design of W engines makes them more complex and expensive to manufacture and maintain than simpler configurations like V engines.
- Specialized Applications: W engines are primarily found in high-end luxury cars and supercars, where the focus is on delivering high performance and a premium driving experience.
Design Differences Between W and V Engines
The design differences between W and V engines are significant and influence their performance, complexity, and applications. Here are the key distinctions:
1. Cylinder Configuration
- V Engine: Consists of two banks of cylinders arranged in a “V” shape, typically at angles ranging from 60 to 90 degrees. Each bank can have a varying number of cylinders (e.g., V6, V8, V12).
- W Engine: Features four banks of cylinders arranged in a “W” shape, which effectively combines two V engines. This allows for a higher cylinder count in a more compact layout.
2. Size and Footprint
- V Engine: Generally more compact than a W engine with fewer cylinders, making it easier to fit in a variety of vehicle designs. The V configuration allows for a relatively low engine height.
- W Engine: Although it has a higher cylinder count, the W engine maintains a compact size compared to traditional designs. However, it is bulkier and can require more space in terms of engine bay design due to its unique shape.
3. Weight
- V Engine: Typically lighter due to its simpler design with fewer components. This weight advantage can contribute to better vehicle handling and fuel efficiency.
- W Engine: Heavier because of the additional cylinder banks and the complexity of the design, which can affect overall vehicle weight and balance.
4. Complexity
- V Engine: Generally simpler in design and easier to manufacture, resulting in lower production costs and more straightforward maintenance.
- W Engine: More complex due to its four banks of cylinders, requiring more intricate engineering and manufacturing processes. This complexity often leads to higher costs for production and maintenance.
5. Firing Order and Balance
- V Engine: Provides a balanced firing order and is designed to minimize vibrations. Many V engines (especially V8s and V12s) are renowned for their smoothness and power delivery.
- W Engine: Offers a balanced firing sequence as well, but with more cylinders, it typically results in even smoother operation and less vibration, providing an exceptionally refined driving experience.
6. Cooling and Lubrication
- V Engine: Cooling and lubrication systems are simpler, as there are only two banks of cylinders to manage, making maintenance easier.
- W Engine: Due to the increased number of components and cylinders, cooling and lubrication systems are more complex, requiring more advanced engineering solutions.
7. Power Output
- V Engine: While capable of high power outputs, especially in larger configurations (like V8 and V12), V engines typically provide a moderate balance of power and efficiency.
- W Engine: Designed to deliver extremely high power outputs, especially in W12 and W16 configurations, making them suitable for high-performance and luxury vehicles where maximum power is desired.
Performance Comparison Between W and V Engines
When comparing the performance of W engines and V engines, several key factors come into play, including power output, torque, efficiency, and overall driving experience. Below is a detailed performance comparison between the two engine types:
1. Torque
- W Engine: W engines tend to produce high torque across a wide RPM range due to their larger displacement and multiple cylinders. This results in rapid acceleration and the ability to maintain power under heavy loads, making them excellent for performance driving.
- V Engine: V engines also deliver substantial torque, particularly in larger configurations like V8s. However, the torque may not be as high as that of comparable W engines. V engines often deliver peak torque at lower RPMs, which can enhance drivability in everyday scenarios.
2. Efficiency
- W Engine: W engines are generally less fuel-efficient due to their higher cylinder count and complexity. The emphasis on performance often results in increased fuel consumption, particularly in high-performance applications where power is prioritized over economy.
- V Engine: V engines can be more fuel-efficient, especially smaller configurations like V6 and V8 engines, which balance performance with economy. Technologies such as cylinder deactivation and turbocharging further enhance fuel efficiency in modern V engines.
3. Smoothness and Refinement
- W Engine: W engines are known for their smooth operation and minimal vibrations, thanks to their high cylinder count and well-balanced design. This results in a refined driving experience, making them popular in luxury vehicles where comfort is paramount.
- V Engine: While V engines, particularly V12s, are also known for smoothness, they can experience more vibration compared to W engines. The performance can vary based on the specific engine configuration and tuning.
4. Driving Experience
- W Engine: The performance of W engines translates to exhilarating driving experiences, with rapid acceleration and impressive power delivery. They often provide a sense of exclusivity and luxury, appealing to enthusiasts seeking high-performance vehicles.
- V Engine: V engines offer a well-rounded driving experience, combining power with good handling and everyday usability. Many V engines are designed for both performance and comfort, making them suitable for a wider range of vehicles, from family cars to sports models.
5. Applications
- W Engine: Primarily used in high-performance and luxury vehicles, W engines excel in applications where extreme power and refinement are necessary. They are found in models like the Bugatti Veyron and Bentley Continental GT.
- V Engine: V engines are versatile and used across a broader spectrum of vehicles, including sedans, SUVs, trucks, and performance cars. They provide a good balance of power, efficiency, and usability, making them a popular choice in the automotive market.
Comparison Table: W Engine vs. V Engine
Here’s a comparison table summarizing the key differences between W engines and V engines:
| Feature | V Engine | W Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Cylinder Banks | 2 banks in a “V” configuration | 4 banks in a “W” configuration |
| Engine Size | Compact | More compact for high cylinder count |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier due to complexity |
| Power Output | Moderate to high | Extremely high (e.g., W16 > 1500 hp) |
| Fuel Efficiency | More fuel-efficient | Less fuel-efficient |
| Complexity | Simpler design, easier to maintain | More complex, harder to maintain |
| Cost | More affordable | More expensive to produce and repair |
| Applications | Widely used in various vehicles | Limited to luxury and high-end cars |
| Smoothness | Smooth but varies by type (V6, V8) | Extremely smooth and refined |
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about W engine vs V engine –
1. What are the main differences between a V engine and a W engine?
The V engine has two banks of cylinders arranged in a “V” shape, whereas a W engine has four banks arranged to resemble two V engines combined. The W engine offers more power in a compact design but is more complex and expensive to maintain.
2. Which engine is more fuel-efficient?
V engines are generally more fuel-efficient because they are simpler and have fewer moving parts. W engines, while powerful, tend to be less fuel-efficient due to their higher cylinder count and complexity.
3. Why are W engines less common than V engines?
W engines are more complex and expensive to manufacture, which limits their use to luxury and high-performance vehicles. V engines are simpler, more versatile, and used in a wide range of cars, trucks, and SUVs.
4. Are W engines more powerful than V engines?
Yes, W engines typically offer more power due to their higher cylinder count. For example, the W16 engine in the Bugatti Chiron delivers over 1,500 horsepower, significantly more than most V engines.
5. Which engine is smoother: V or W?
W engines tend to be smoother due to their higher cylinder count and more balanced power delivery. However, V engines, particularly V12s, also offer excellent smoothness and refinement.
Conclusion
Both W engines and V engines have their unique advantages and applications. While V engines are more common and versatile, W engines provide exceptional power and refinement in a compact design, making them ideal for luxury and high-performance vehicles. Choosing between the two depends largely on the desired balance between performance, complexity, and cost.