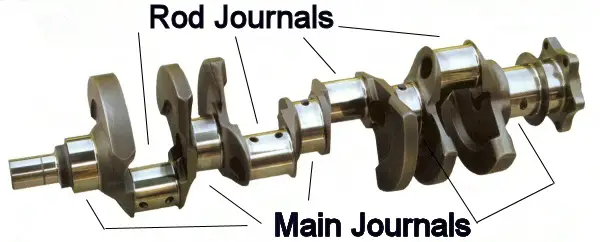
Crankshaft journals are precision-machined surfaces on the crankshaft that interact with the engine’s bearings, allowing smooth rotation and efficient power transmission. They come in two types: main journals, which support the crankshaft within the engine block, and rod journals, which connect to the pistons via connecting rods.
Crankshaft journals are integral components of an internal combustion engine’s crankshaft, playing a critical role in the engine’s operation. These journals are the surfaces within the crankshaft that interact with the engine’s bearings, allowing for the smooth rotation and transmission of power. Understanding the function, types, and maintenance of crankshaft journals is essential for anyone involved in engine repair, rebuilding, or performance tuning.
Contents
The Anatomy of a Crankshaft
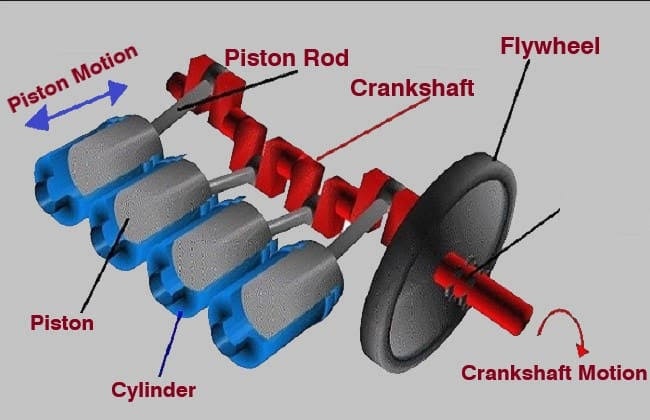
Before delving into crankshaft journals, it’s essential to understand the basic anatomy of a crankshaft. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft within the engine that converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which ultimately powers the vehicle’s wheels. It is a critical component of the engine’s bottom end and is responsible for transferring the force generated by combustion to the drivetrain.
A crankshaft consists of the following key components:
- Main Journals: These are the surfaces where the crankshaft is supported within the engine block. They rotate within the main bearings and help maintain the alignment of the crankshaft.
- Rod Journals (Crank Pins): These are offset from the crankshaft’s centerline and connect to the connecting rods, which link the crankshaft to the pistons. The rod journals are responsible for converting the pistons’ linear motion into rotational motion.
- Crank Webs: These are the arms of the crankshaft that connect the main journals to the rod journals. They contribute to the crankshaft’s overall balance and strength.
- Counterweights: These are strategically placed weights on the crankshaft designed to balance the rotating assembly, reducing vibrations and stress on the engine.
What Are Crankshaft Journals?
Crankshaft journals are the precision-machined surfaces of the crankshaft that rotate within the engine’s bearings. They are critical in ensuring the smooth operation of the crankshaft, minimizing friction and wear, and maintaining proper alignment within the engine block. There are two primary types of crankshaft journals:
- Main Journals:
- Main journals are located along the length of the crankshaft and are positioned in line with the engine’s crankcase. These journals sit within the main bearings, which are housed in the engine block. The primary function of the main journals is to support the crankshaft and allow it to rotate freely while maintaining alignment with the engine block. Proper lubrication is crucial for the main journals to function effectively, as they operate under high loads and speeds.
- Rod Journals (Crank Pins):
- Rod journals, also known as crank pins, are located on the crankshaft’s throws, which are offset from the main journals. These journals connect to the connecting rods, which link the crankshaft to the pistons. The rod journals are responsible for converting the reciprocating motion of the pistons into the rotational motion of the crankshaft. Like main journals, rod journals require precise machining and proper lubrication to reduce friction and wear.
Importance of Crankshaft Journals
Crankshaft journals are critical to the engine’s performance, reliability, and longevity. Their importance can be understood through the following points:
- Load-Bearing Capacity:
- Crankshaft journals must withstand significant forces generated during engine operation, including the explosive force of combustion and the inertial forces of the rotating assembly. The journals are designed to distribute these forces evenly across the bearings, minimizing wear and preventing damage to the crankshaft and engine block.
- Friction Reduction:
- The journals, in conjunction with the bearings, play a vital role in reducing friction within the engine. Proper lubrication and the smooth surface finish of the journals ensure that the crankshaft can rotate with minimal resistance, enhancing engine efficiency and reducing heat generation.
- Alignment and Balance:
- The journals help maintain the alignment of the crankshaft within the engine block, ensuring smooth and consistent operation. Misalignment or excessive wear on the journals can lead to vibrations, increased friction, and even catastrophic engine failure.
- Oil Clearance:
- The gap between the crankshaft journals and the bearings, known as oil clearance, is critical for maintaining a thin film of lubricant that separates the metal surfaces. This oil film prevents metal-to-metal contact, reduces wear, and helps dissipate heat generated by friction.
Types of Crankshaft Journals
Crankshaft journals can vary in design and construction depending on the type of engine and its intended use. Some of the common types of crankshaft journals include:
- Fully-Counterweighted Journals:
- In engines with fully counterweighted crankshafts, each crank pin or rod journal has a corresponding counterweight on the crankshaft. These counterweights help balance the rotating assembly, reducing vibrations and stress on the engine’s bearings. Fully-counterweighted journals are commonly found in high-performance and heavy-duty engines.
- Knife-Edged Journals:
- Knife-edged crankshaft journals have a streamlined, sharp-edged design that reduces windage and drag within the crankcase. This design is often used in racing engines to minimize frictional losses and improve high-speed performance. However, knife-edged journals may require more frequent maintenance and inspection due to their reduced surface area and increased susceptibility to wear.
- Cross-Drilled Journals:
- Cross-drilled journals feature oil passages that are drilled through the crankshaft, allowing for improved oil flow and distribution to the bearings. This design enhances lubrication and cooling, particularly in high-performance or heavily loaded engines. Cross-drilled journals are commonly used in racing and high-performance applications.
- Fillet-Radiused Journals:
- Fillet-radiused crankshaft journals have a rounded fillet at the junction between the journal and the crankshaft web. This design reduces stress concentrations in the crankshaft, improving its strength and resistance to cracking. Fillet-radiused journals are often used in engines that experience high loads or frequent changes in RPM.
Maintenance of Crankshaft Journals
Proper maintenance and inspection of crankshaft journals are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of an engine. Here are some key considerations:
- Regular Inspection:
- During engine rebuilds or routine maintenance, it is important to inspect the crankshaft journals for signs of wear, scoring, pitting, or damage. Any irregularities in the journal surfaces can lead to increased friction, poor lubrication, and potential engine failure.
- Measurement of Journal Diameter:
- The diameter of the crankshaft journals measured using a micrometer to ensure they are within the manufacturer’s specifications. Undersized or worn journals may require regrinding or replacement to restore proper clearance and function.
- Surface Finish:
- The surface finish of the journals is critical for maintaining proper oil clearance and reducing friction. Journals should have a smooth, polished surface with no scratches or grooves. If the surface finish is compromised, the journals may need to be polished or re-machined.
- Lubrication:
- Proper lubrication is essential for the longevity of crankshaft journals. Regular oil changes, using the correct type of oil, and maintaining proper oil pressure are crucial for preventing journal wear and ensuring smooth operation.
- Regrinding and Undersized Bearings:
- If the journals are worn or damaged, they can often be re-ground to a smaller diameter and paired with undersized bearings. This process restores the journals’ smooth surface and proper oil clearance, extending the life of the crankshaft.
Related Article
Crankshaft Journal Size Charts
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about the crankshaft journals
1. What are the main types of crankshaft journals?
The main types of crankshaft journals are main journals, which support the crankshaft within the engine block, and rod journals (crank pins), which connect to the connecting rods and convert the pistons’ linear motion into rotational motion.
2. How do crankshaft journals affect engine performance?
Crankshaft journals affect engine performance by reducing friction, maintaining proper alignment, and distributing load forces evenly. Properly functioning journals are essential for smooth engine operation and longevity.
3. Can crankshaft journals be repaired if damaged?
Yes, damaged crankshaft journals can often be repaired through a process called regrinding, where the journal surface is machined to a smaller diameter and paired with undersized bearings.
4. What causes crankshaft journals to wear out?
Crankshaft journals can wear out due to factors such as insufficient lubrication, contamination, excessive engine loads, and improper maintenance. Regular inspection and proper lubrication are key to preventing wear.
5. How can I maintain my crankshaft journals?
To maintain crankshaft journals, regularly inspect them for wear and damage, measure their diameter, ensure proper lubrication, and follow the manufacturer’s maintenance recommendations. If necessary, regrind worn journals and use undersized bearings.
Conclusion
Crankshaft journals are essential components of an engine’s crankshaft, responsible for supporting the crankshaft, reducing friction, and ensuring proper alignment within the engine block. Understanding the different types of journals, their functions, and the importance of proper maintenance is crucial for anyone involved in engine repair, rebuilding, or performance tuning.
By paying attention to the condition of crankshaft journals and following best practices for maintenance and inspection, engine builders and mechanics can ensure the longevity and reliability of the engine.