A radial tire is a type of tire in which the layers of cords are arranged radially, running perpendicular to the tire’s circumference, providing enhanced stability and performance. Radial tires have become the standard in the automotive industry due to their superior handling, fuel efficiency, and overall durability.
With the cords positioned in a radial pattern, radial tires are able to distribute weight evenly, resulting in a smoother and more comfortable ride. They also offer improved traction and grip, making them ideal for various weather conditions. Whether you’re driving on a highway or tackling off-road terrain, radial tires are designed to deliver optimal performance, making them a popular choice for vehicles of all types.
Credit: www.tireagent.com
Contents
The Evolution of Tires: A Brief History
The development of the radial tire is a significant milestone in the history of automotive engineering. To fully appreciate its impact, it’s essential to understand the evolution of tire technology:
- Early Tires: The first tires were solid rubber, used primarily for horse-drawn carriages. These tires were durable but offered a rough ride.
- Pneumatic Tires: Invented by John Boyd Dunlop in 1888, pneumatic (air-filled) tires significantly improved comfort and performance by cushioning the ride.
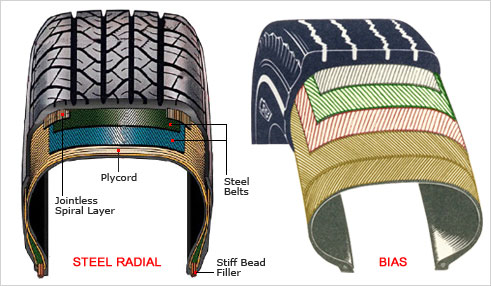
- Bias-Ply Tires: Before radial tires, bias-ply (or cross-ply) tires were the standard. In these tires, the layers (plies) of fabric were laid diagonally, overlapping each other, providing durability and load-bearing capacity. However, they had significant drawbacks, including poor handling, less comfort, and a shorter lifespan.
The limitations of bias-ply tires led to the invention of radial tires, which revolutionized tire technology and became the industry standard.
What is a Radial Tire?
A radial tire is a type of pneumatic tire in which the cord plies are arranged perpendicularly to the direction of travel, running radially from the center of the wheel to the outer edge. This construction differs significantly from the older bias-ply design, where the plies crisscross each other at an angle.
The key components of a radial tire include:
Radial Ply Cords: The main feature of a radial tire is the arrangement of its ply cords. These cords are typically made of materials like polyester, steel, or fiberglass and are positioned at a 90-degree angle to the tire’s direction of travel. This layout allows the sidewall and the tread to function independently, enhancing performance.
Steel Belts: Radial tires are reinforced with steel belts situated under the tread. These belts provide strength, reduce rolling resistance, and improve fuel efficiency and tread wear.
Tread and Sidewall: The tread and sidewall are separate entities in radial tires, allowing for improved flexibility in the sidewall and better contact with the road through the tread. This separation enhances the tire’s overall performance, including handling, stability, and ride comfort.
Advantages of Radial Tires
Radial tires offer several benefits over bias-ply tires, making them the preferred choice for most vehicles today:
Improved Fuel Efficiency
Radial tires have lower rolling resistance due to their construction. The steel belts under the tread reduce the energy required to keep the tire rolling, resulting in better fuel efficiency.
Enhanced Ride Comfort
The flexible sidewalls of radial tires absorb shocks and vibrations more effectively, providing a smoother and more comfortable ride compared to bias-ply tires.
Better Handling and Stability
The independent functioning of the tread and sidewall allows radial tires to maintain better contact with the road, improving handling and stability. This characteristic is particularly beneficial during high-speed driving and cornering.
Longer Tread Life
The steel belts and radial construction help to distribute weight evenly across the tire’s footprint, reducing uneven wear. This design results in longer tread life and better overall performance.
Improved Traction
Radial tires provide better traction on both wet and dry surfaces due to the uniform pressure distribution and larger contact patch. This feature enhances safety and performance in various driving conditions.
Applications of Radial Tires
Radial tires are now used in almost all types of vehicles, ranging from passenger cars to heavy-duty trucks. Let’s explore some of the key applications:
Passenger Cars: Radial tires are the standard for passenger cars due to their superior comfort, handling, and fuel efficiency. They are suitable for city driving, highway cruising, and even light off-road conditions.
Light Trucks and SUVs: Radial tires for light trucks and SUVs are designed to handle heavier loads and provide stability without compromising comfort. They offer better traction and durability for both on-road and off-road driving.
Commercial Vehicles: For commercial vehicles such as buses, trucks, and trailers, radial tires provide better fuel efficiency and longevity, which are crucial for reducing operating costs. The robust construction of radial tires also helps to withstand the high demands of commercial use.
Agricultural and Off-Road Vehicles: Specialized radial tires are available for agricultural and off-road vehicles. These tires are designed to provide excellent traction, durability, and reduced soil compaction, benefiting both the vehicle and the environment.
Radial vs. Bias-Ply Tires: A Comparison
While radial tires are the standard today, understanding the differences between radial and bias-ply tires is essential for making an informed choice in specific applications.
| Feature | Radial Tires | Bias-Ply Tires |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Ply cords run radially, steel belts under the tread | Ply cords crisscross at an angle |
| Ride Comfort | Superior ride comfort due to flexible sidewalls | Stiffer ride due to rigid sidewalls |
| Handling and Stability | Better handling and stability | Less precise handling |
| Tread Life | Longer tread life | Shorter tread life |
| Load Capacity | Lower load capacity | Higher load capacity for heavy-duty applications |
| Applications | Most passenger and commercial vehicles | Heavy-duty trucks, off-road, and specialty vehicles |
When to Choose Bias-Ply Tires: While radial tires are superior in most aspects, bias-ply tires are still used in certain heavy-duty and off-road applications where maximum load capacity and resistance to damage are critical.
How to Choose the Right Radial Tire
Selecting the right radial tire for your vehicle depends on several factors:
Vehicle Type
Choose a tire designed specifically for your vehicle type, whether it’s a passenger car, SUV, truck, or commercial vehicle. Each category of tire is engineered to meet the unique demands of the vehicle and its typical usage.
Driving Conditions
Consider the typical driving conditions you encounter. For example, if you drive mostly on highways, look for tires with low rolling resistance and good fuel efficiency. If you drive in winter conditions, consider winter radial tires with better traction on snow and ice.
Load and Speed Ratings
Check the load and speed ratings of the tire to ensure it meets your vehicle’s specifications. The load rating indicates the maximum weight the tire can safely carry, while the speed rating indicates the maximum speed the tire can handle.
Tread Pattern
The tread pattern affects the tire’s performance in different conditions. All-season tread patterns are suitable for a variety of conditions, while specialized tread patterns are available for winter, off-road, and high-performance driving.
Brand and Warranty
Choose reputable brands that offer good warranties. A reliable warranty can be a lifesaver if you encounter issues with the tire.

Credit: www.dunlopaircrafttyres.co.uk
How to Maintain Radial Tires
Proper maintenance can significantly extend the life of your radial tires and ensure optimal performance. Here are some maintenance tips:
Regular Inspection: Check your tires regularly for signs of wear, damage, or irregularities. Look for cracks, bulges, or foreign objects embedded in the tread.
Tire Rotation: Rotate your tires every 5,000 to 8,000 miles to ensure even wear. Proper rotation patterns depend on whether your vehicle is front-wheel drive, rear-wheel drive, or all-wheel drive.
Wheel Alignment and Balancing: Have your wheels aligned and balanced regularly to prevent uneven wear and ensure smooth handling.
Proper Inflation: Maintain the correct tire pressure as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. Underinflated or overinflated tires can lead to poor handling, increased wear, and reduced fuel efficiency.
Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the tire’s load capacity. Overloading can cause excessive wear and increase the risk of a blowout.

Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about radial tires –
1. What makes radial tires different from bias-ply tires?
Radial tires have plies that run perpendicular to the direction of travel, with steel belts under the tread for added strength and stability. This construction offers better handling, comfort, and durability compared to bias-ply tires, which have crisscrossed plies.
2. Are radial tires suitable for off-road use?
Yes, radial tires are available in off-road variants designed to provide excellent traction, durability, and reduced soil compaction. However, for extreme off-road conditions, bias-ply tires may be preferred due to their superior load-bearing capacity and resistance to punctures.
3. How do I know if my vehicle has radial tires?
Most modern vehicles come equipped with radial tires. You can check the sidewall of the tire for the letter “R” in the tire size (e.g., P215/65R15). The “R” indicates that it is a radial tire.
4. Can I mix radial and bias-ply tires on my vehicle?
Mixing radial and bias-ply tires on the same vehicle is not recommended, as it can lead to unpredictable handling and stability issues. If you need to use different types of tires, always consult your vehicle manufacturer’s guidelines.
5. How often should I replace my radial tires?
The lifespan of radial tires varies depending on usage, maintenance, and driving conditions. Generally, radial tires should be replaced every 6-10 years, even if there is still tread left, due to the natural aging of the rubber. Regularly inspect your tires and replace them if you notice signs of excessive wear or damage.
Conclusion
Radial tires have transformed the automotive world, offering numerous advantages over traditional bias-ply tires. Their unique construction provides better fuel efficiency, improved handling, longer tread life, and enhanced ride comfort. Whether you’re driving a passenger car, an SUV, a truck, or even a commercial vehicle, radial tires are designed to meet your needs with superior performance and safety.
Understanding the benefits and characteristics of radial tires will help you make informed decisions when choosing, maintaining, and replacing your tires. By selecting the right radial tire and following proper maintenance practices, you can enjoy a smooth, safe, and efficient driving experience.