Choosing the right battery size for the car involves matching the battery group size, cold cranking amps (CCA), and reserve capacity (RC) to your vehicle’s specifications, which can typically be found in the owner’s manual. It’s essential to use the correct group size to ensure proper fit and connection.
Choosing the correct battery size is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of the vehicle. When it comes to selecting a battery for the car, it’s essential to consider factors such as the climate you live in and the electronic features of the vehicle.
A properly sized battery ensures that the car starts reliably and functions smoothly. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of choosing the right battery size for the car and provide tips on how to determine the correct size. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of why the size of the car’s battery matters and how to make the best choice for the vehicle.

Credit: www.walmart.com
Contents
Car Battery
Before delving into the specifics of car battery sizes, it’s important to understand some basic concepts related to car batteries.
1. Battery Types
There are several types of car batteries available, each with its own set of characteristics:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: The most common type found in conventional vehicles. They are reliable and affordable but require maintenance and have a shorter lifespan compared to newer technologies.
- AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) Batteries: A more advanced type of lead-acid battery that offers better performance, longer life, and is maintenance-free. They are suitable for vehicles with high electrical demands or start-stop systems.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Primarily used in electric and hybrid vehicles, these batteries are lightweight and have a longer lifespan but are more expensive.
2. Battery Group Size
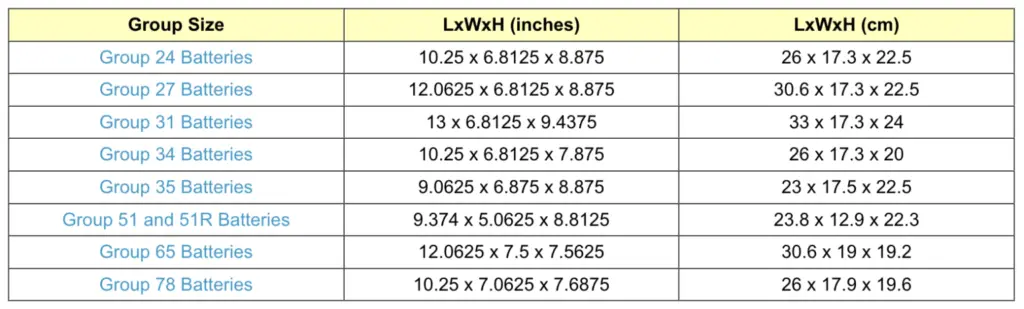
Battery group size is a standard classification that indicates the physical dimensions of the battery, including its length, width, height, and terminal placement. It is essential to choose a battery with the correct group size to ensure it fits properly in the battery tray and connects securely to the vehicle’s terminals.
Common group sizes include:
- Group 24/24F: Often used in large cars and SUVs.
- Group 35: Common in Japanese cars like Honda and Toyota.
- Group 48 (H6): Found in many European and American vehicles.
- Group 94R (H7): Used in various European and American models.
3. Cold Cranking Amps (CCA)
CCA measures a battery’s ability to start an engine in cold temperatures. It indicates the number of amps a battery can deliver at 0°F for 30 seconds while maintaining a voltage of at least 7.2 volts. A higher CCA rating is important in colder climates to ensure reliable starting performance.
4. Reserve Capacity (RC)
Reserve capacity refers to how long a fully charged battery can supply power at 25 amps before dropping below 10.5 volts. It is an indicator of how long the battery can run essential systems if the alternator fails.
How to Choose the Right Battery Size for the Car
Selecting the correct battery size involves considering various factors, from the vehicle’s specifications to the driving habits. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Check the Owner’s Manual
The first and most reliable source for determining the correct battery size is the vehicle’s owner’s manual. It will list the recommended battery group size, CCA, and other specifications. Using a battery that meets or exceeds these recommendations ensures compatibility and optimal performance.
2. Identify the Battery Group Size
As mentioned earlier, the battery group size is crucial for fitting. It’s typically listed on the battery label and can also be found on battery retailer websites or in-store catalogs. If you’re unsure, the current battery’s label in the car will often have this information.
3. Consider Cold Cranking Amps (CCA)
Choose a battery with a CCA rating that matches or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommendation. A higher CCA is beneficial for vehicles operated in colder climates as it ensures the battery can provide sufficient power to start the engine in low temperatures.
4. Look at Reserve Capacity (RC)
While not always specified in the owner’s manual, RC is important for ensuring the battery can support electrical systems if the alternator fails. For vehicles with high electrical demands or those used for long periods with the engine off, a higher RC is advantageous.
5. Factor in Additional Features
If the vehicle has features like a start-stop system, heated seats, or a premium sound system, consider upgrading to an AGM battery. These batteries handle the higher electrical loads better and have a longer lifespan in such applications.
6. Consider Driving Conditions and Habits
If you drive in extreme weather conditions or frequently take short trips that don’t allow the battery to recharge fully, a battery with higher CCA and RC may be beneficial. Additionally, if the vehicle sits idle for long periods, consider a battery maintainer or a deep-cycle battery.

Credit: www.batteriesplus.com
Common Battery Sizes and Applications
Here are some of the most common battery group sizes and their typical applications:
1. Group 24/24F
- Application: Large cars, SUVs, trucks, and some light commercial vehicles.
- Specifications: CCA ranges from 500 to 800, with varying reserve capacities.
- Typical Vehicles: Toyota Camry, Nissan Altima, and Ford Taurus.
2. Group 35
- Application: Compact and midsize cars, including many Japanese makes and models.
- Specifications: CCA typically ranges from 500 to 700, with moderate reserve capacity.
- Typical Vehicles: Honda Accord, Toyota Corolla, Subaru Outback.
3. Group 48 (H6)
- Application: Many European and American vehicles, including luxury models.
- Specifications: High CCA and RC, making them suitable for high-demand electrical systems.
- Typical Vehicles: BMW 3 Series, Mercedes-Benz C-Class, Cadillac CTS.
4. Group 94R (H7)
- Application: High-performance and luxury vehicles with high electrical demands.
- Specifications: Higher CCA and RC, suitable for start-stop systems.
- Typical Vehicles: Audi A4, Volkswagen Passat, Jeep Grand Cherokee.
5. Group 65
- Application: Large trucks, SUVs, and commercial vehicles.
- Specifications: High CCA and RC to handle large engines and high electrical loads.
- Typical Vehicles: Ford F-150, Chevrolet Silverado, Dodge Ram.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about the car batteries –
1. Can I use a different group size battery in my car?
While it is possible to use a different group size, it is not recommended unless you are certain it will fit properly and meet the vehicle’s specifications. Using the wrong size can lead to poor performance, safety issues, and potential damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
2. How do I know when my car battery needs to be replaced?
Signs that the battery may need replacing include slow engine crank, dimming headlights, and frequent need for jump-starts. If the battery is more than 3-5 years old, it’s a good idea to have it tested regularly.
3. What happens if I use a battery with lower CCA?
Using a battery with lower CCA than recommended can lead to poor starting performance, especially in cold weather. It may struggle to start the engine, and in severe cases, it could fail altogether in low temperatures.
4. Are AGM batteries worth the extra cost?
AGM batteries are worth the investment if the vehicle has high electrical demands, a start-stop system, or you drive in extreme conditions. They offer better performance, longer lifespan, and are maintenance-free compared to conventional lead-acid batteries.
5. Can I install a car battery myself?
Yes, installing a car battery is generally straightforward if you follow proper safety precautions. Ensure the vehicle is off, disconnect the negative terminal first, and reconnect it last when installing the new battery. If you are unsure, it’s best to have a professional handle the installation.
Conclusion
Selecting the right battery size for the car is crucial for ensuring reliable performance and avoiding potential issues down the road. By understanding the vehicle’s requirements and considering factors such as battery type, group size, CCA, and RC, you can make an informed decision that meets your needs.