When your power steering stops working, you may experience difficulty turning the steering wheel, especially at low speeds, making driving challenging. Common causes include low or leaking power steering fluid, a failing power steering pump, or issues with the electric power steering system.
Power steering is a critical feature in modern vehicles, making it easier to maneuver and control your car with minimal effort. When power steering fails, driving becomes challenging, particularly at lower speeds or when parking. Understanding the reasons behind power steering failure, how to diagnose the issue, and potential solutions can help you address the problem effectively and ensure your vehicle remains safe and comfortable to drive.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the common causes of power steering failure, how to diagnose the problem, and the steps you can take to fix it.
Contents
What is Power Steering and Why is it Important?
Power steering is a system that uses hydraulic or electric power to assist drivers in steering the vehicle. Without power steering, turning the steering wheel would require significant physical effort, especially at low speeds. This system is crucial for enhancing driver comfort and safety, making it easier to control the vehicle in various driving conditions.
There are two main types of power steering systems:
- Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS): Uses hydraulic pressure generated by a pump driven by the engine to assist in steering.
- Electric Power Steering (EPS): Uses an electric motor instead of hydraulic pressure to assist in steering.
Signs That Power Steering Not Working
Before diving into the causes, it’s important to recognize the symptoms of power steering failure. Here are some common signs that your power steering system is not functioning properly:
- Difficulty Turning the Wheel: The steering wheel becomes hard to turn, especially at low speeds.
- Steering Wheel Feels Stiff: The wheel doesn’t return to its center position smoothly after turning.
- Noisy Steering: You hear squealing, groaning, or whining noises when turning the steering wheel.
- Steering Fluid Leaks: You notice puddles of fluid under your vehicle, which could indicate a leak in the power steering system.
- Dashboard Warning Light: Some vehicles have a power steering warning light that illuminates when there’s an issue with the system.
Common Causes of Power Steering Failure
Power steering issues can arise from various components within the system. Understanding these causes can help you diagnose and address the problem more effectively.
1. Low or Leaking Power Steering Fluid (Hydraulic Systems)
Description: In hydraulic power steering systems, fluid is essential for generating the pressure needed to assist in steering. If the fluid level is low or if there’s a leak, the system cannot function properly.
Signs:
- Difficulty turning the wheel.
- Whining or groaning noises when steering.
- Visible fluid leaks under the car, often around the steering rack or pump.
Causes:
- Worn or damaged seals in the steering pump, rack, or hoses.
- Aged or deteriorated hoses that have become brittle and cracked.
- Loose or damaged hose connections.
Solution:
- Check the power steering fluid level and top it up if necessary.
- Inspect the system for leaks and replace any damaged hoses or seals.
- If the fluid is contaminated (dark or gritty), consider flushing and replacing the fluid.
2. Power Steering Pump Failure
Description: The power steering pump is responsible for circulating the hydraulic fluid throughout the system. If the pump fails, the system loses pressure, making it difficult to steer.
Signs:
- Whining or squealing noises when the engine is running.
- Stiff or unresponsive steering, especially at low speeds.
- Fluid foaming or bubbling in the reservoir.
Causes:
- Wear and tear over time leading to internal damage.
- Running the system with low or contaminated fluid, which can damage the pump.
- Belt slippage due to a worn or loose drive belt.
Solution:
- Inspect the power steering pump for signs of damage or wear.
- Replace the power steering pump if it’s not functioning correctly.
- Ensure the drive belt is in good condition and properly tensioned.
3. Electric Power Steering (EPS) Issues
Description: In vehicles with EPS, an electric motor provides the steering assistance. Problems with the EPS system can lead to a loss of steering assistance.
Signs:
- Stiff steering or loss of power assistance, often accompanied by a warning light on the dashboard.
- Intermittent loss of power steering, especially during startup or at lower speeds.
Causes:
- Faulty EPS motor or electronic control unit (ECU).
- Electrical issues such as blown fuses, loose connections, or wiring problems.
- Software glitches or failures in the vehicle’s computer system.
Solution:
- Check the vehicle’s electrical system for blown fuses or loose connections.
- If the issue persists, a diagnostic scan may be necessary to identify faults in the EPS system.
- Replace the EPS motor or ECU if found to be defective.
4. Steering Rack and Pinion Failure
Description: The steering rack and pinion are critical components that translate the rotational movement of the steering wheel into the linear motion needed to turn the wheels. Failure in these parts can cause steering problems.
Signs:
- Clunking or knocking noises when turning the wheel.
- Uneven steering effort, with the wheel feeling harder to turn in one direction than the other.
- Fluid leaks around the steering rack.
Causes:
- Worn or damaged internal components within the rack and pinion.
- Leaks from worn seals or gaskets in the steering rack.
- Contaminated or low power steering fluid causing wear.
Solution:
- Inspect the steering rack and pinion for signs of wear or damage.
- Replace the steering rack if it’s worn out or leaking.
- Ensure the power steering fluid is clean and at the correct level.
5. Steering Column Issues
Description: The steering column connects the steering wheel to the rest of the steering system. Problems with the column can cause steering difficulties.
Signs:
- Difficulty turning the wheel.
- Unusual noises when turning the wheel.
- Play or looseness in the steering wheel.
Causes:
- Worn or damaged bearings within the steering column.
- Misalignment or damage to the steering column components.
- Issues with the tilt or telescopic mechanisms in adjustable steering columns.
Solution:
- Inspect the steering column for wear, misalignment, or damage.
- Replace any worn bearings or damaged components.
- Realign the steering column if necessary.
6. Drive Belt Problems
Description: In hydraulic systems, the power steering pump is typically driven by a belt connected to the engine. If the belt is damaged or loose, the pump may not operate efficiently, leading to steering issues.
Signs:
- Squealing noise from the engine bay, especially during startup or when turning the wheel.
- Stiff steering, particularly at low speeds.
- Visible wear or fraying on the drive belt.
Causes:
- Aged or worn drive belt that has become loose or frayed.
- Misaligned or damaged belt pulleys.
- Improper belt tension causing slippage.
Solution:
- Inspect the drive belt for signs of wear or damage.
- Replace the belt if it’s worn or damaged.
- Ensure the belt tension is correct and that the pulleys are properly aligned.
Diagnosing Power Steering Problems
Diagnosing power steering issues can sometimes be straightforward, especially if there are visible signs like leaks or noises. However, more complex problems, particularly with EPS systems, may require specialized tools and knowledge. Here’s a general approach to diagnosing power steering problems:
1. Visual Inspection
- Check the Fluid Level: Start by checking the power steering fluid level. Low fluid is a common cause of steering issues.
- Look for Leaks: Inspect the hoses, pump, and steering rack for any signs of leaks.
- Examine the Drive Belt: Ensure the drive belt is in good condition and properly tensioned.
2. Listen for Noises
- Whining or Squealing: Noises while turning the wheel could indicate a problem with the power steering pump or a slipping belt.
- Clunking or Knocking: These noises might point to issues with the steering rack or suspension components.
3. Check the Steering Feel
- Stiff Steering: Difficulty turning the wheel is a key indicator of power steering failure. Note whether the stiffness occurs at all times or only under certain conditions (e.g., low speeds, high speeds).
- Intermittent Loss of Assistance: If the power steering cuts out intermittently, this could indicate an electrical issue in EPS systems.
4. Use Diagnostic Tools
- Diagnostic Scanner: For vehicles with EPS, using a diagnostic scanner can help identify error codes related to the power steering system.
- Pressure Gauge: In hydraulic systems, a pressure gauge can measure the output of the power steering pump to ensure it’s functioning properly.
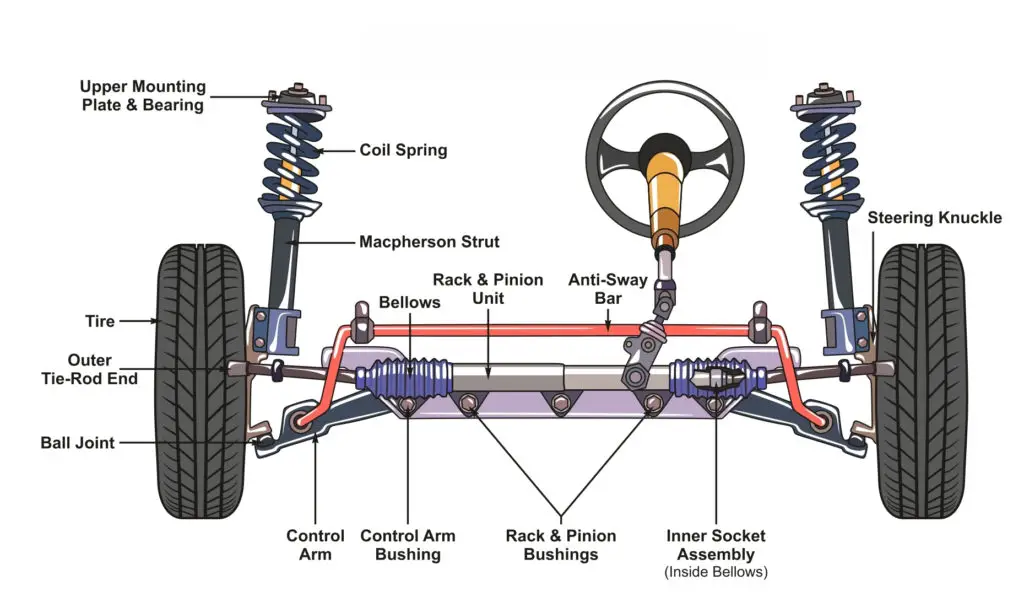
Credit: carparts.com
How to Fix Power Steering Problems
Once you’ve identified the cause of the power steering failure, it’s time to address the issue. Here’s how to fix common problems:
1. Refill or Replace Power Steering Fluid
- If the fluid is low, top it up with the recommended type of power steering fluid.
- If the fluid is dirty or contaminated, flush the system and refill it with fresh fluid.
2. Repair or Replace Leaking Components
- Replace any damaged hoses, seals, or gaskets that are causing leaks.
- If the steering rack or pump is leaking, it may need to be replaced or rebuilt power steering pump.
3. Replace the Power Steering Pump or Motor
- If the pump or motor is failing, replace it with a new or rebuilt unit.
- Ensure the drive belt is in good condition and properly tensioned.
4. Address Electrical Issues
- Replace any blown fuses, and check for loose connections or damaged wiring in EPS systems.
- If the EPS motor or ECU is faulty, it may need to be replaced.
5. Realign or Replace Steering Components
- Replace worn bearings, and realign the steering column if necessary.
- Replace the steering rack or rack and pinion assembly if it’s worn out or damaged.
Preventing Power Steering Problems
Preventing power steering issues is largely about regular maintenance and timely repairs. Here are some tips to keep your power steering system in good shape:
- Regularly Check Fluid Levels: Make it a habit to check the power steering fluid level and top it up as needed.
- Inspect for Leaks: Periodically inspect the steering system for any signs of leaks.
- Replace the Fluid: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for replacing the power steering fluid, typically every 50,000 to 100,000 miles.
- Maintain the Drive Belt: Ensure the drive belt is in good condition and properly tensioned.
- Address Issues Promptly: If you notice any signs of power steering problems, address them immediately to prevent further damage.
Conclusion
Power steering failure can significantly impact the safety and comfort of your vehicle. By understanding the common causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing how to diagnose and fix issues, you can keep your power steering system in top condition.