A serpentine belt is a single, continuous belt in a vehicle’s engine that powers essential components like the alternator, power steering, and air conditioning. It transfers power from the engine to these systems and needs regular inspection to avoid breakdowns.
In the world of automotive parts, the serpentine belt is a true workhorse. Though often overlooked, this essential component keeps many of your vehicle’s crucial systems running smoothly. Understanding what a serpentine belt does, how it works, and how to maintain it can help prevent breakdowns and extend your vehicle’s life. In this post, we’ll dive deep into the serpentine belt’s purpose, function, maintenance, and replacement.
Contents
What is a Serpentine Belt?
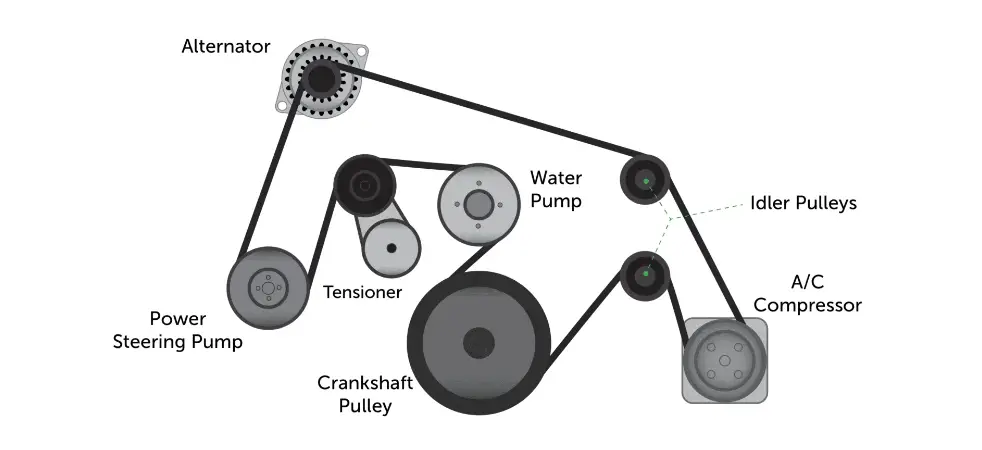
A serpentine belt, also known as a drive belt, is a long, continuous belt in the engine that winds its way around various pulleys, much like a snake, hence the name “serpentine.” Its primary function is to transfer power from the engine’s crankshaft pulley to various auxiliary components, such as the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, and air conditioning compressor.
The serpentine belt is typically made from durable rubber or synthetic material, designed to withstand high temperatures, friction, and wear. Unlike older engines that used multiple belts to drive each component, modern engines often rely on a single serpentine belt, making the system more efficient and less prone to failure.
Components Driven by a Serpentine Belt
The serpentine belt connects to several key components in the engine, all essential for the smooth operation of the vehicle:
- Alternator: Powers the vehicle’s electrical system and charges the battery while the engine is running.
- Power Steering Pump: Provides hydraulic pressure for the power steering system, allowing for easier steering.
- Air Conditioning Compressor: Powers the A/C system, providing cool air inside the cabin.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant through the engine to regulate temperature and prevent overheating (in some vehicles, the water pump is driven by the timing belt instead).
- Radiator Fan: Some vehicles use a serpentine belt to power the radiator fan, which helps cool the engine.
By driving these components, the serpentine belt ensures that critical systems like the electrical, cooling, and steering systems operate properly.
How a Serpentine Belt Works
When the engine is running, it drives the crankshaft pulley, which, in turn, moves the serpentine belt. As the belt moves, it rotates the pulleys attached to various engine components. This rotation drives these components, allowing them to perform their designated functions. The serpentine belt follows a specific path set by the vehicle manufacturer, usually indicated on a diagram under the vehicle’s hood.
The Role of the Belt Tensioner
The belt tensioner is a component designed to keep the serpentine belt at the right level of tension. Most modern belt tensioners are spring-loaded, automatically adjusting tension as needed. A faulty tensioner can cause belt slippage, noise, and accelerated wear on the belt. Replacing a failing tensioner is often necessary when installing a new belt.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about serpentine belts –
Q1: What happens if my serpentine belt breaks while driving?
A: If the serpentine belt breaks while driving, you may lose power steering, your battery may stop charging, and your engine could overheat if the water pump is affected. It’s essential to pull over safely and seek assistance as soon as possible to avoid engine damage.
Q2: Can I drive my car without a serpentine belt?
A: Driving without a serpentine belt isn’t recommended. Without it, your vehicle’s critical systems, such as the alternator, power steering, and air conditioning, won’t function, which could quickly lead to engine overheating and battery depletion.
Q3: How long does a serpentine belt typically last?
A: The average lifespan of a serpentine belt ranges from 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on driving conditions, vehicle make, and the quality of the belt. Regular inspections are key to ensuring it remains in good condition.
Q4: Can a worn serpentine belt affect fuel efficiency?
A: Yes, a worn serpentine belt can cause certain components, like the alternator or power steering pump, to work harder, which in turn increases fuel consumption. Replacing a worn belt can help improve fuel efficiency and vehicle performance.
Q5: How much does it cost to replace a serpentine belt?
A: The cost to replace a serpentine belt varies by vehicle type, labor rates, and parts. On average, it can range from $75 to $200, with labor costs making up a significant portion of the total. Replacing the belt tensioner, if needed, may increase the cost.
Conclusion
The serpentine belt may not be as well-known as other car components, but it plays a crucial role in the overall functionality of your vehicle. Understanding its function, maintenance requirements, and replacement intervals can go a long way toward preventing breakdowns and ensuring that your vehicle remains in optimal condition. If you’re experiencing signs of a failing belt, consult a professional mechanic for an inspection and, if necessary, replace it promptly.