Brake Assist is a safety feature that helps vehicles achieve maximum braking force during emergency stops. It works by detecting sudden and hard braking and automatically increases brake pressure to prevent accidents.
Brake Assist is an essential safety feature designed to enhance a vehicle’s braking performance during emergency situations. By providing additional brake pressure when it detects sudden and hard braking, Brake Assist helps drivers reduce stopping distances and avoid potential collisions.
This feature is particularly valuable in high-stress driving scenarios, providing an extra layer of protection and peace of mind for drivers and passengers alike. Understanding how Brake Assist works and its benefits can help drivers make informed decisions about vehicle safety and choose models equipped with this valuable feature.
Credit: carfromjapan.com
Contents
What is Brake Assist?
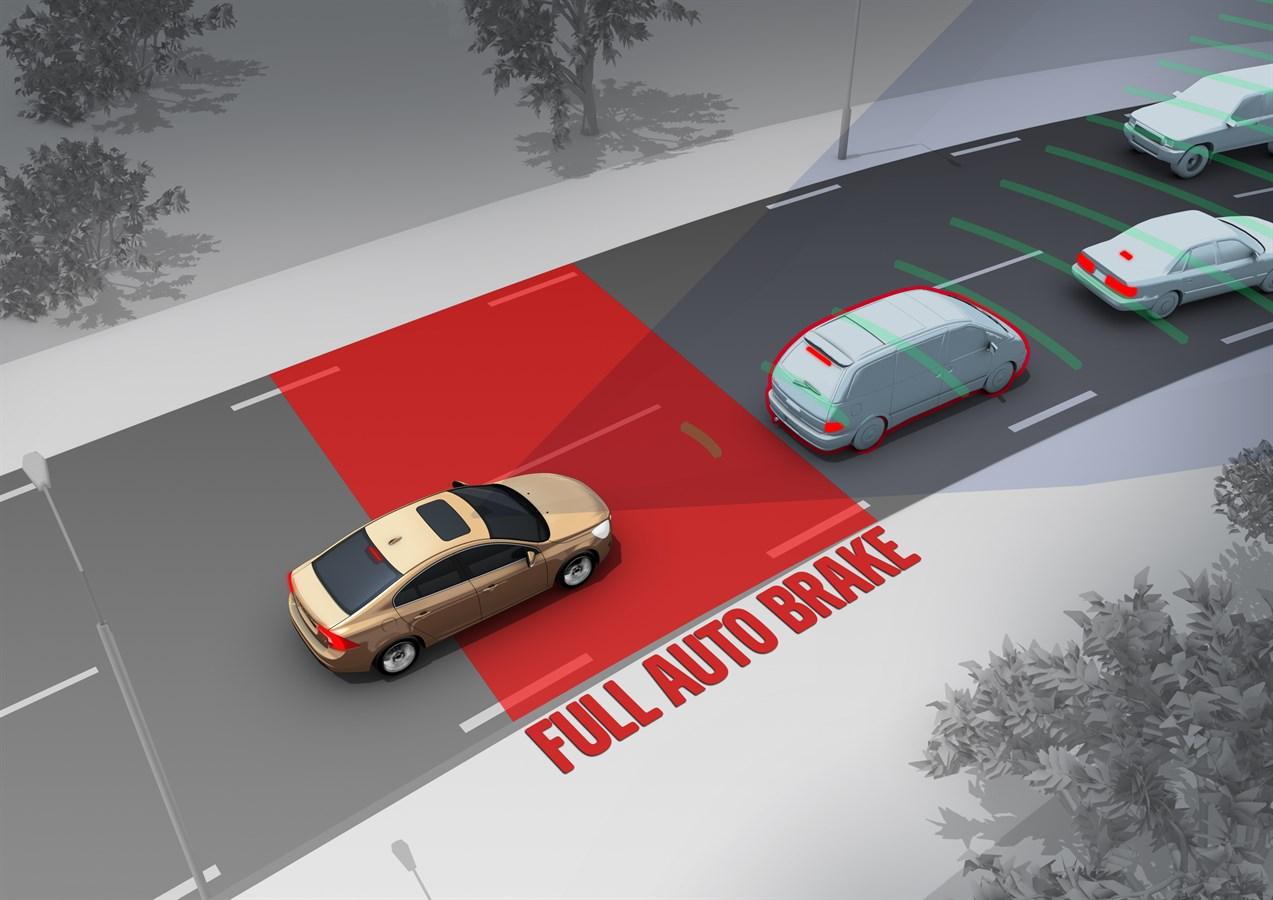
Brake Assist (BA) is an advanced driver assistance system (ADAS) designed to help drivers achieve maximum braking force during emergency stops, even if they do not fully apply the brake pedal. The system works by detecting when a driver is making a panic stop and automatically increasing brake pressure to ensure the vehicle comes to a stop as quickly as possible.
Many drivers, in moments of emergency, fail to apply enough pressure to the brake pedal, resulting in a longer stopping distance. Brake Assist compensates for this by sensing the urgency of the braking and applying additional force to reduce the stopping distance and potentially avoid a collision.
Development of Brake Assist
The concept of Brake Assist was first introduced in the late 1990s, with Mercedes-Benz pioneering its development. Research showed that a significant percentage of drivers, even in emergency situations, did not press the brake pedal hard enough to fully engage the anti-lock braking system (ABS). This insight led to the creation of Brake Assist, a system that could detect panic braking and automatically apply full braking pressure.
Since then, Brake Assist has become a standard safety feature in many vehicles around the world and is often integrated with other systems such as ABS and Electronic Stability Control (ESC).
How Does Brake Assist Work?
The Brake Assist system operates through a combination of sensors and electronic control units (ECUs). These components work together to monitor the speed and force with which the driver presses the brake pedal and determine whether the action is indicative of an emergency. The process can be broken down into the following steps:
- Pedal Speed Detection: Brake Assist is designed to recognize when the brake pedal is pressed quickly but not forcefully enough. A normal braking action involves a gradual increase in pressure, but an emergency stop often involves a rapid press.
- Interpreting the Brake Pedal Force: The system compares the speed of pedal movement to predefined thresholds. If the driver presses the pedal very quickly, the system assumes the driver is attempting an emergency stop.
- Applying Maximum Brake Pressure: Once the system determines that emergency braking is required, it immediately activates the Brake Assist mechanism. It rapidly boosts brake pressure to the maximum level, ensuring that the vehicle decelerates as quickly as possible.
- Engagement of ABS: Since the driver may not fully engage the ABS system themselves, Brake Assist ensures that the ABS is triggered to prevent wheel lockup and maintain steering control.
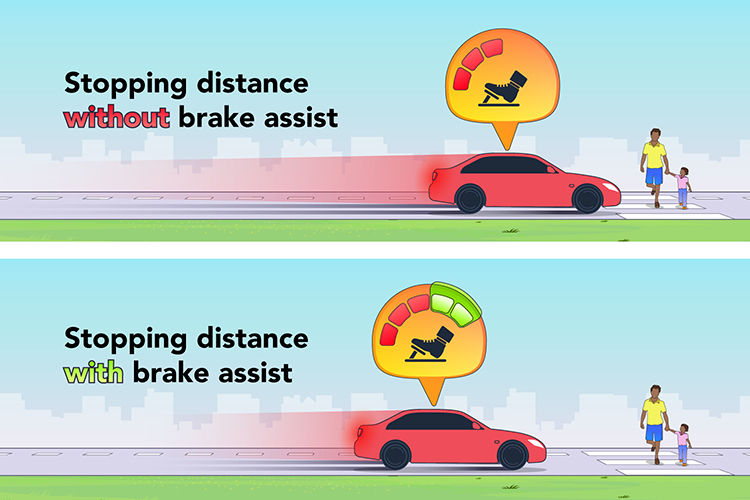
- Reduction of Stopping Distance: By applying additional braking force, Brake Assist reduces the stopping distance, potentially avoiding a collision or mitigating the severity of an accident.
Brake Assist vs. Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS)
It’s important to understand the distinction between Brake Assist and ABS. While both systems work together to enhance braking performance, they serve different functions:
- Brake Assist: Its primary purpose is to detect emergency braking and apply full braking force if the driver doesn’t press the pedal hard enough. It ensures that the driver gets maximum braking power in a panic stop.
- ABS: The Anti-Lock Braking System prevents the wheels from locking up under heavy braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. ABS doesn’t increase braking force; instead, it modulates the brake pressure to avoid wheel lockup.
In essence, Brake Assist helps drivers who may not apply enough braking force in an emergency, while ABS helps drivers maintain control during hard braking.
Benefits of Brake Assist
The introduction of Brake Assist has brought significant benefits to vehicle safety, particularly in emergency scenarios. Here’s a closer look at the advantages:
- Reduced Stopping Distance: By ensuring maximum braking force, Brake Assist can drastically shorten stopping distances. This reduction can mean the difference between a near-miss and a collision.
- Increased Driver Confidence: Knowing that Brake Assist is present allows drivers to feel more secure, knowing the system will support them during critical situations.
- Enhanced Safety in Panic Stops: Brake Assist is particularly useful in situations where a driver’s reflexes may not be fast enough or they may hesitate to press the brakes firmly, such as when a pedestrian or vehicle suddenly enters their path.
- Integrated with Other Safety Systems: Brake Assist works in tandem with ABS, ESC, and Traction Control Systems (TCS), providing a comprehensive safety net for drivers. These systems ensure that the vehicle maintains stability and control even under extreme braking.
- Widely Available: Over the years, Brake Assist has become a standard feature in many vehicles, from economy cars to high-end luxury models. This widespread availability means more drivers can benefit from this life-saving technology.
Real-World Applications of Brake Assist
Brake Assist has been instrumental in preventing or reducing the severity of collisions in many real-world scenarios:
- Highway Emergencies: When traffic comes to a sudden halt on a busy highway, drivers may not always have enough time to react fully. Brake Assist engages quickly to reduce stopping distances, helping prevent rear-end collisions.
- Urban Driving: In crowded city streets, pedestrians, cyclists, and vehicles often appear unexpectedly. Brake Assist ensures that even hesitant or less experienced drivers can stop their vehicle in time.
- Wet and Slippery Conditions: When driving on wet or icy roads, drivers may not apply the brakes hard enough due to fear of skidding. Brake Assist, combined with ABS, ensures maximum braking power while preventing wheel lockup.
Credit: tc.canada.ca
The Future of Brake Assist
As vehicle technology continues to evolve, Brake Assist is also undergoing advancements. In some modern systems, Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) is integrated with Brake Assist, allowing the car to detect potential collisions and apply the brakes without driver input if necessary. Additionally, adaptive brake assist systems are being developed, which can take into account variables such as vehicle speed, distance to obstacles, and road conditions.
With the rise of autonomous driving technology, Brake Assist is expected to play a pivotal role in ensuring that vehicles can stop safely in emergencies, regardless of whether a human or machine is behind the wheel.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some FAQs about brake assist –
Does Brake Assist activate every time I brake?
No, Brake Assist is designed to activate only during emergency braking situations, when it detects rapid but insufficient brake pedal pressure.
Is Brake Assist the same as Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB)?
No, Brake Assist requires the driver to initiate braking, while AEB can apply the brakes automatically without driver input if a potential collision is detected.
Can Brake Assist work without ABS?
No, Brake Assist works in conjunction with ABS to ensure that full braking power is applied while preventing wheel lockup. Both systems are essential for safe emergency braking.
How do I know if my car has Brake Assist?
Many modern vehicles come equipped with Brake Assist as a standard feature, especially in vehicles with ABS. You can check your car’s owner’s manual or consult the manufacturer to verify if your vehicle has this feature.
Can Brake Assist malfunction?
While rare, any electronic system can experience issues. If there is a problem with your Brake Assist system, you may see a warning light on your dashboard, and the vehicle should be taken to a mechanic for diagnosis.
Conclusion
Brake assist technology has become an essential feature in modern vehicles. It serves as a safety net for drivers, helping them avoid accidents by providing additional stopping power. This system is designed to work in conjunction with the driver’s foot brake, making it an ideal solution for emergency situations.
As technology continues to improve, we can expect to see more advanced brake assist systems in the future, making driving safer for everyone on the road. Remember, always prioritize safety while driving and invest in vehicles equipped with the latest safety technology, such as brake assist.